How to Scrape Amazon Reviews
Amazon is the go-to destination for online shoppers – and with that comes a treasure trove of customer reviews. These reviews provide invaluable insights for businesses looking to understand consumer preferences, researchers tracking market trends, and shoppers making well-informed decisions. In this guide, we’ll explore the types of data you can extract from Amazon reviews, outline various scraping methods, and show you how to efficiently scrape reviews using Python and our powerful residential proxies.
Dominykas Niaura
Last updated: Aug 04, 2025
10 min read
What are Amazon reviews?
Amazon reviews are user-generated feedback provided by customers who have purchased and used products available on Amazon's platform. These reviews play a crucial role in the eCommerce ecosystem by offering insights into product quality, functionality, and user satisfaction. They help potential buyers make informed decisions and enable sellers to understand customer experiences and areas for improvement.
Each Amazon review typically consists of several key data points:
- Review ID. A unique identifier assigned to each review.
- Title. A brief headline summarizing the review, often including the star rating and a concise opinion.
- Author. The username or display name of the customer who wrote the review.
- Rating. The star rating given by the reviewer on a scale from 1 to 5.
- Content. The main body of the review where the customer shares their detailed thoughts and experiences.
- Timestamp. The date and location when and where the review was posted.
- Profile ID. A unique identifier associated with the reviewer's Amazon profile.
- Verified purchase status. Indicates whether the reviewer purchased the product through Amazon, adding credibility to the review.
- Helpful count. The number of other users who found the review helpful.
- Product attributes. Specific details about the product variant being reviewed, such as color, size, or style.
These components allow customer sentiment analysis, competitor monitoring, product performance tracking, and gaining insights into consumer behavior. By examining these data points, businesses can identify trends, address issues, and enhance their products or services to better meet customer needs.
Scraping Amazon customer reviews: best methods
Amazon reviews scraping typically involves using a service, automated tools, or software to programmatically extract customer review data from Amazon's product pages. Here’s a list of the best ways you can get Amazon reviews data:
1. Buying datasets from third-party services
One option for obtaining Amazon review data is to use third-party services that offer pre-collected datasets. There are several companies that specialize in aggregating large volumes of data from various sources, including eCommerce platforms like Amazon.
By purchasing these datasets, you can access extensive review information without the need to build your own scraper or manage the complexities of data extraction.
These services often provide the data in structured, ready-to-use formats, which can save you significant time and resources. Also, if it’s a reputable provider, this data is collected ethically and in compliance with all relevant laws and Amazon’s terms of service.
2. Using web scraping tools
If you're looking for a plug-and-play solution and don't want to write any code, third-party web scraping tools might still do the trick. However, most of them now struggle with Amazon reviews due to updated anti-bot measures. Many previously reliable APIs have lost access or become unstable.
Unless the tool supports custom proxy integration and active maintenance like Decodo's Review Scraper API, it's safer to stick with your own solution.
3. Building a custom solution
For most use cases, a custom-built scraper is the most flexible and future-proof option. It gives you full control over what data you collect, how often, and in what format. Whether you're targeting specific products, running sentiment analysis, or integrating review data into a broader pipeline, a tailored scraper setup lets you build around your exact needs.
The best approach is to combine a lightweight Python scraper (e.g., using Requests, httpx, or Selenium) and combine it with proxies to maintain stable access, bypass anti-bot systems, and stay in control of your data extraction process. This setup is flexible, scriptable, and easy to adapt as Amazon’s page structure or anti-bot logic evolves.
Why proxies are necessary for stable scraping
When scraping Amazon reviews, proxies are extremely helpful. Amazon has robust anti-bot mechanisms that can quickly block your IP address if it detects unusual behavior, such as sending too many requests within a short time. By routing your traffic through different IP addresses, proxies help you distribute requests and avoid hitting rate limits or triggering CAPTCHAs.
For the best results, it's recommended to use residential proxies. Residential IPs are associated with real internet service providers, making your traffic appear more like a typical user browsing from home. Ideally, use a rotating proxy service that automatically assigns a new IP address with each request, providing maximum coverage and minimizing the chance of bans.
At Decodo, we offer residential proxies with a high success rate (99.86%), a rapid response time (<0.6s), and extensive geo-targeting options (195+ worldwide locations). Here's how easy it is to get a plan and your proxy credentials:
- Head over to the Decodo dashboard and create an account.
- On the left panel, click Residential.
- Choose a subscription, Pay As You Go plan, or opt for a 3-day free trial.
- In the Proxy setup tab, select the location, session type, and protocol according to your needs.
- Copy your proxy address, port, username, and password for later use. Alternatively, you can click the download icon in the lower right corner of the table to download the proxy endpoints (10 by default).
Easy way to scrape Amazon product reviews
If you want to collect Amazon product reviews reliably and on your own terms, the best method right now is to use a custom Python script with residential proxies. This gives you full control, keeps your data fresh, and avoids relying on unstable third-party APIs (which often lose access anyway). Let’s walk through a simple setup.
1. Install prerequisites
Before running the Amazon review scraper, make sure you have Python 3.8+ installed. Then, you'll need to install a few Python libraries. The script uses both built-in Python modules and some external packages:
- time – for delays between requests
- random – for randomizing delays
- json – for saving review data
- logging – for error messages
- re – for regex pattern matching
- Requests – for making HTTP requests to Amazon
- lxml – for parsing HTML and using XPath selectors
Use this command to install the required external libraries:
2. Set up proxy credentials
The script requires proxy credentials to avoid getting blocked by Amazon. Once you have your Decodo proxy credentials, you'll need to update several variables in the usage section at the bottom of the script:
- Replace 'YOUR_PROXY_USERNAME' with your proxy username
- Replace 'YOUR_PROXY_PASSWORD' with your proxy password
- In the line "proxy = f"http://{username}:{password}@gate.decodo.com:7000," you can replace gate.decodo.com:7000 with your specific proxy address and port depending on the parameters you configure in Decodo's dashboard
3. Configure target product
You'll need to specify which Amazon product you want to scrape reviews from by updating the product URL. Change 'https://www.amazon.com/dp/B07ZF8T63K' to whatever product you want to analyze – just copy the URL from any Amazon product page.
This script focuses on scraping the top reviews that are visible directly on a product’s main page – not the full list of reviews. Amazon has made it harder to access all reviews without logging in, and many detailed review pages now load dynamically using JavaScript. By targeting the top visible reviews, we avoid those complications and still get valuable, recent feedback without dealing with authentication or headless browsers.
4. Run the script
Copy and save the Amazon reviews scraping script below as a Python file (e.g., amazon_scraper.py), then run it after updating your proxy credentials and target product URL.
This scraper is built with a Python class that collects top reviews from Amazon product pages. It uses realistic headers, timed delays, and residential proxies to blend in like a real user and avoid getting blocked.
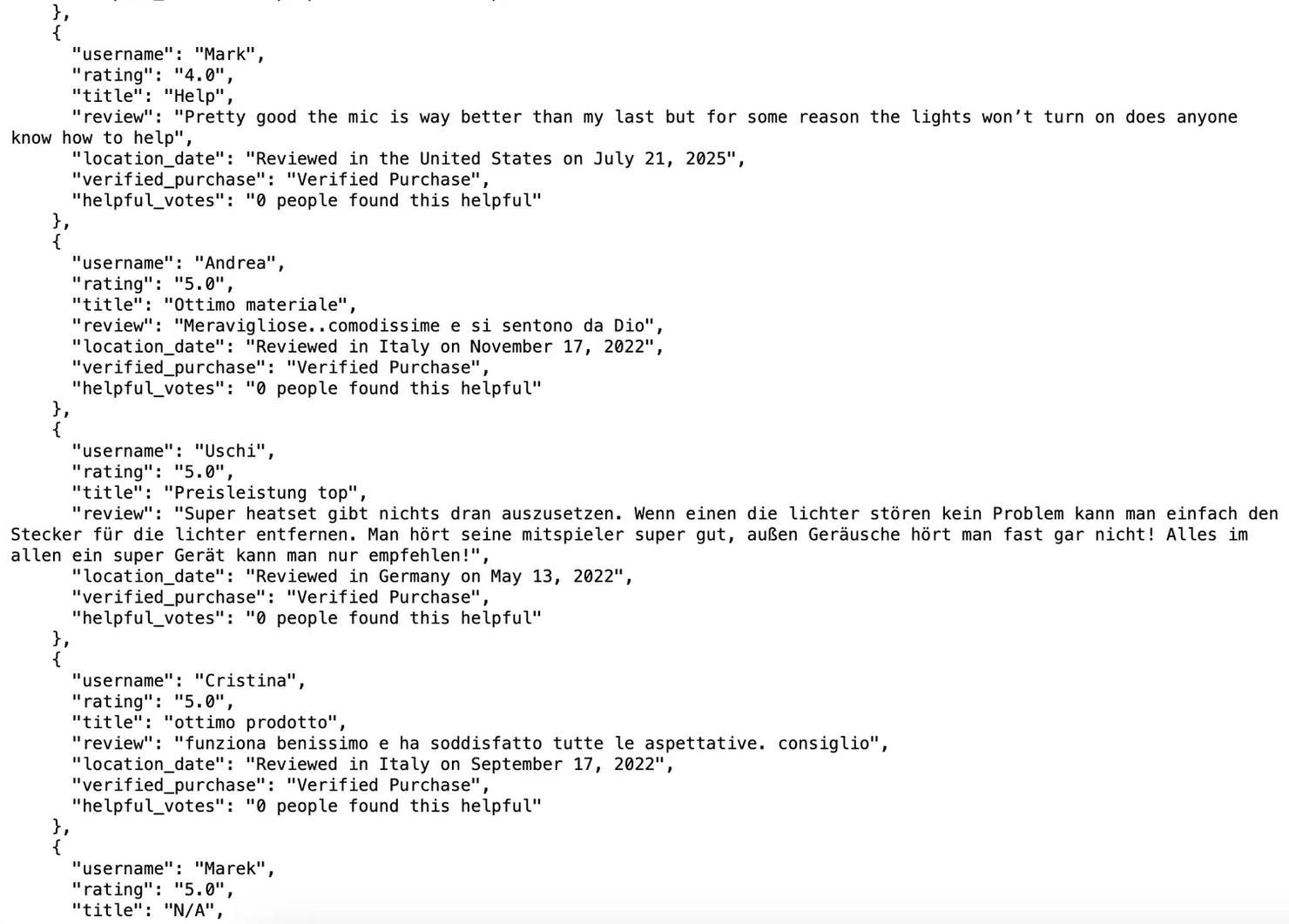
The script focuses on the top reviews shown directly on the product page and pulls key info (username, rating, title, text, date, location, verified status, and helpful vote count) using XPath selectors you can adjust if Amazon’s layout changes.
It also filters out duplicates, detects CAPTCHAs, and saves everything to a JSON file – plus shows a quick preview in your terminal.
Bottom line
With a simple Python script and residential proxies, you can reliably scrape Amazon product reviews in just a few minutes. This approach gives you full control over the data, avoids common scraping issues, and works well at scale. It's a solid option for collecting customer feedback, tracking sentiment, or analyzing product performance.
Get residential proxies for Amazon
Claim your 3-day free trial of residential proxies to collect Amazon reviews with full feature access.
About the author

Dominykas Niaura
Technical Copywriter
Dominykas brings a unique blend of philosophical insight and technical expertise to his writing. Starting his career as a film critic and music industry copywriter, he's now an expert in making complex proxy and web scraping concepts accessible to everyone.
Connect with Dominykas via LinkedIn
All information on Decodo Blog is provided on an as is basis and for informational purposes only. We make no representation and disclaim all liability with respect to your use of any information contained on Decodo Blog or any third-party websites that may belinked therein.