How to Scrape Google Lens: A Step-By-Step Guide
Google Lens has revolutionized how we interact with visual content – it allows users to search the web using images rather than text queries. This powerful visual search engine can identify objects, text, landmarks, products, and much more from uploaded images. In this guide, we'll explore the types of data that can be scraped from Google Lens, examine various methods for extracting this information, and demonstrate how to efficiently collect visual search results using our Web Scraping API.
Dominykas Niaura
Last updated: Jul 24, 2025
10 min read
What is Google Lens?
Google Lens is an advanced visual search engine that uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to analyze and understand images.
This powerful tool can identify objects (such as plants, animals, and everyday stuff), recognize famous landmarks and provide historical information, extract text from images (signs, documents, and handwritten notes), translate text in real-time, find similar products and shopping options, discover visually related content across the web.
Users can simply point their camera at an object or upload an image to receive detailed information about what they're viewing. These capabilities have made Google Lens a go-to tool for students, travelers, shoppers, and professionals who need quick visual information.
Why scrape Google Lens results?
Google Lens scraping is the automated process of extracting search results and related data from Google's visual search platform. By programmatically submitting images to Google Lens, you can gather comprehensive information and leverage it for various business and research applications.
Using web scraping tools and scripts, it's possible to efficiently analyze large volumes of images and extract the rich data that Google Lens provides. This practice offers several practical applications:
- Product identification and price comparison. eCommerce businesses can automatically identify products from images and track pricing across different platforms, enabling competitive analysis and dynamic pricing strategies.
- Training data for machine learning models. Developers can build comprehensive datasets for computer vision applications, object recognition systems, and AI training by collecting Google Lens results across thousands of images.
- Building interactive or informational apps. Create applications that offer users instant visual search capabilities, product recommendations, or educational content based on uploaded images.
- Automating research or cataloging tasks. Researchers and analysts can streamline the process of studying visual trends, content relationships, and object recognition patterns across the web without manual analysis.
What data can be scraped from Google Lens?
When scraping data from Google Lens, you can extract several key pieces of information for each result:
- Related URLs. Direct links to web pages where similar or related content appears.
- Page titles. Descriptive text from web pages containing related visual content.
- Source domains. The websites hosting the related content, useful for assessing credibility.
- Thumbnail images. Visual previews of related content for quick similarity assessment.
- Position rankings. The order of results, indicating relevance to your submitted image.
- Visual metadata. Information about identified objects, text, or landmarks in the image.
By collecting this data, you can build reverse image search systems, conduct visual content research, track product appearances, or analyze visual trends and patterns.
Challenges of scraping Google Lens
While Google Lens provides valuable visual search data, scraping it comes with several technical and ethical challenges that developers and businesses must navigate carefully.
Dealing with CAPTCHAs and anti-bot measures
Google employs sophisticated detection systems to identify automated requests, including CAPTCHAs, rate limiting, and behavioral analysis. These measures can block scraping attempts and require advanced techniques to bypass, such as rotating user agents, implementing human-like delays, and solving visual challenges.
Need for proxies or specialized APIs
Since Google monitors for suspicious activity and can block repeated requests from the same IP, a reliable scraping setup should use rotating proxies to distribute traffic and avoid detection.
Specialized scraping APIs or headless browser automation tools are also often needed to handle the JavaScript-heavy, dynamic interface of Google Lens. These tools typically include CAPTCHA bypassing, proxy handling, and error handling to ensure consistent performance.
Ethical and responsible usage considerations
Scraping Google Lens should be done responsibly by respecting server resources, maintaining reasonable request rates, avoiding the collection of personal or sensitive information, and ensuring that scraped data isn’t misused. Users should consider the impact of their scraping activities on Google's infrastructure and other users' experience with the platform.
5 methods for scraping Google Lens
Scraping Google Lens can be accomplished through various methods, each suitable for different needs and levels of technical expertise. In this section, we'll explore how to extract data from Google Lens using some common approaches.
1. Google’s official APIs
While there’s no public Google Lens API, Google offers other tools that cover similar use cases:
- Cloud Vision API. Detects objects, labels, landmarks, and text in images.
- Custom Search JSON API. Allows image search using public image URLs (not uploads).
These APIs return structured data in JSON and are suitable for developers seeking programmatic image analysis, though they do not replicate Google Lens’s full functionality. Usage is subject to quotas and fees.
2. Headless browsers
The web version of Google Lens can be automated using tools like Selenium, which simulate a user uploading an image and viewing the results. This method involves:
- Automating browser actions (uploading, clicking, extracting data).
- Dealing with JavaScript-heavy content and anti-bot mechanisms like CAPTCHAs.
It’s a powerful option for advanced users, but it may break without warning.
3. Alternative image analysis with OpenCV or Pillow
If your goal is to analyze images locally rather than scrape Google’s results, libraries like OpenCV and Pillow can be useful. These tools allow for:
- Object detection
- Pattern matching
- OCR (when combined with tools like Tesseract)
While they don’t interact with Google Lens or retrieve its data, they can help you build custom solutions for visual recognition tasks.
4. Dedicated Google Lens scraper
For a more efficient and hassle-free solution, you can use a dedicated scraper like Decodo's Google Lens scraper API. This API is designed to simplify the data-gathering process from various web sources, including Google Lens. It handles all the complexities, such as image upload handling, rotating proxies, bypassing CAPTCHAs, and parsing the data into a structured format. This means you don't have to worry about technical challenges or extensive coding.
We offer a ready-made scraper that can extract data from Google Lens and doesn't require much or any coding experience. With our API, you can quickly and reliably collect the visual search data you need for your projects.
Step-by-step guide: scraping Google Lens results
Let's say we want to analyze a movie poster to find similar content, related merchandise, or identify the film across different platforms. For that, we'll submit an image URL to Google Lens and extract comprehensive data about related content. Collecting this information manually would be time-consuming, so we'll use an automated web scraping tool called Web Scraping API.
1. Get Web Scraping API
Log in to your Decodo dashboard, navigate to Pricing under the Scraping APIs column on the left panel, and choose a subscription plan or claim a 7-day free trial to test our service.
2. Find the ready-made scraper
A ready-made scraper is a pre-configured template within our API that offers target-specific scraping with appropriate parameter options and parsing capabilities. To find the Google Lens ready-made scraper, follow these steps:
- Access the Scraper tab.
- Click on Choose Target.
- Select Google Lens.
You now have the scraper set to target Google Lens!
3. Configure your scraping request
Enter your image URL (the image you want to analyze), and configure parameters like JavaScript rendering, parsing, device type, and browser. The scraper accepts direct image URLs and will submit them to Google Lens for analysis.
In our case, since we're analyzing a luxury handbag, we'll enter a direct URL to the Louis Vuitton Neverfull image as our query parameter.
4. Send your request and export the response
Once you've set your scraping parameters, click the Send Request button or use the scheduling options to have the response delivered to your email, webhook, or Google Drive at your preferred interval.
Alternatively, you can copy the request code in cURL, Node.js, or Python and integrate it into your development environment. Check out our documentation to adjust the parameters to suit your needs. Our request code in Python looks like this:
To keep things readable in your terminal, you can also use Python's pprint module to format the response instead of printing raw JSON with long Base64-encoded image data. You'll get a clean, human-friendly preview of the structured results by slightly adjusting the code like this:
After clicking Send Request when using our scraper in the dashboard, you'll receive the response in JSON or CSV format shortly, which you can copy or export.
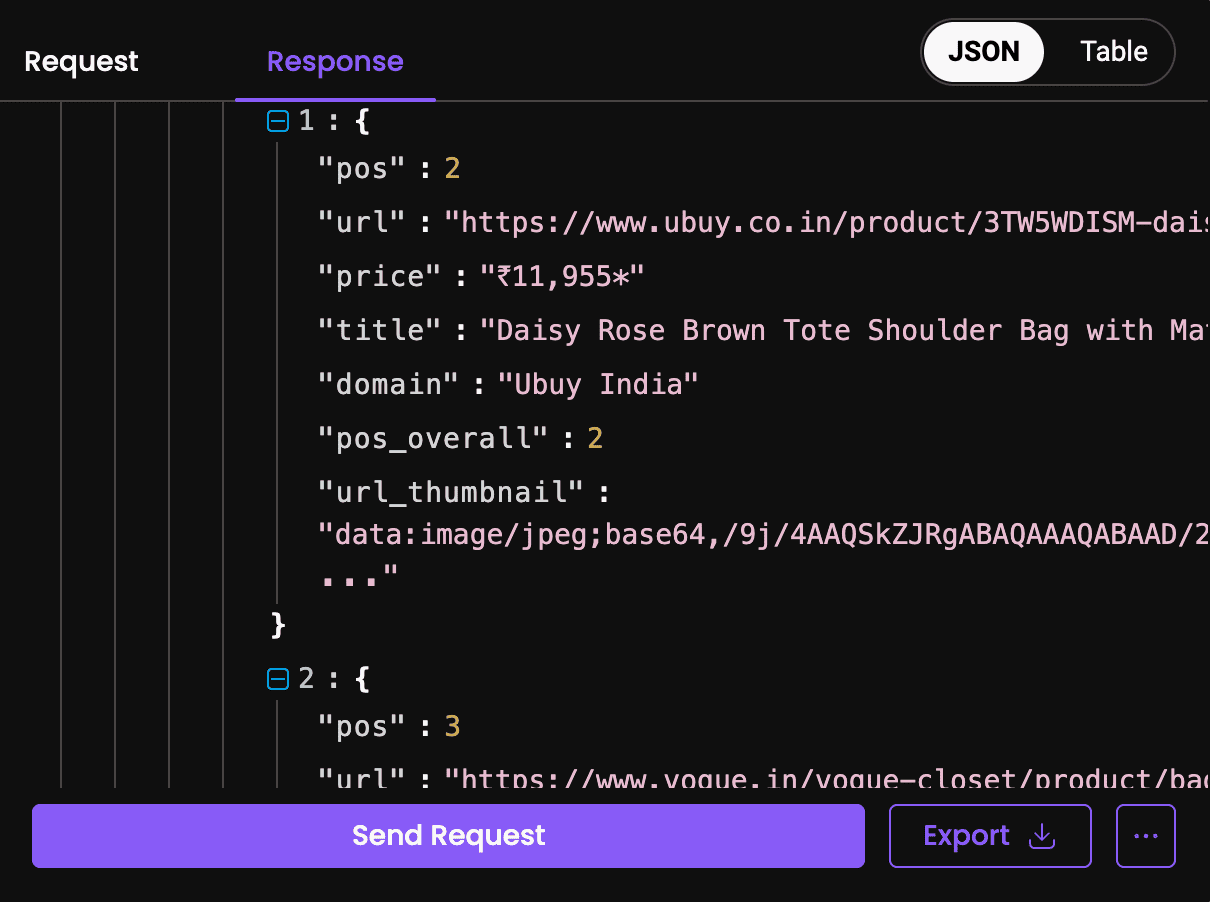
We now have comprehensive data about our analyzed handbag! It includes related retail listings, similar luxury products, pricing information across different platforms, and contextual information that we can use for price comparison, authenticity verification, inventory tracking, or any other luxury retail project.
Best practices for Google Lens scraping
When scraping Google Lens, it's essential to follow these crucial best practices to ensure your activities are ethical, legal, and efficient:
- Optimize your scraping strategy. Limit your request rate to avoid overwhelming servers and triggering anti-scraping measures. Utilize rotating proxies to distribute requests and mimic natural browsing behavior.
- Maintain data quality. Validate your collected data for accuracy and completeness. Remove duplicates and organize your dataset in a structured format like JSON or CSV for easy analysis.
- Ensure security and privacy. Protect your system from potential risks associated with web scraping. Securely store your data to prevent unauthorized access and comply with privacy regulations.
- Use reliable tools. Leverage reputable scraping tools like Web Scraping API, which handles complexities like proxy management and data parsing, enhancing efficiency and compliance.
By following these best practices, you can effectively scrape Google Lens while minimizing risks and maintaining high data quality.
To sum up
Scraping Google Lens provides valuable visual search data for projects like reverse image search, product identification, content analysis, and computer vision research. Using our ready-made Web Scraping API scraper, you can quickly and easily extract data from Google Lens without extensive coding, ideal for users seeking a low-code or no-code solution to efficiently gather the visual search insights they need while adhering to best practices.
About the author

Dominykas Niaura
Technical Copywriter
Dominykas brings a unique blend of philosophical insight and technical expertise to his writing. Starting his career as a film critic and music industry copywriter, he's now an expert in making complex proxy and web scraping concepts accessible to everyone.
Connect with Dominykas via LinkedIn
All information on Decodo Blog is provided on an as is basis and for informational purposes only. We make no representation and disclaim all liability with respect to your use of any information contained on Decodo Blog or any third-party websites that may belinked therein.