Fake IP Address: What Is It and Why Shouldn't You Use It?
When we scale businesses, do research, or just scroll leisurely, it's always a good idea to be clued up on online security. Whatever your reasons for running your eyes over a web browser are, anonymity and privacy are two pretty important players here. The thing is that any browser, website, system, or network can see our IP address. Some of them might even log your IP address and track it. In this blog post, we’ll go over the dangers of using free software, fake IPs, and the illegal aspects of using IP information.
Benediktas Kazlauskas
Last updated: Nov 05, 2025
6 min read

What does your IP address tell about you?
Your IP address acts like a digital ID, disclosing details about your location and online activity. It can reveal:
- Your country, city, and area code.
- Your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
This transparency is both a necessity and a vulnerability, as it enables connections and exposes some personal data layers.
Who can trace your IP address?
While you might think that only you and your ISP can trace your IP address, the truth is that your unique numerical code is exposed to a range of other parties:
- Employers track IPs to monitor staff activity or restrict unauthorized access.
- Law enforcement uses IPs to trace cybercrimes and investigate illegal activity.
- Advertisers collect IP-based data for targeted ads and location-specific marketing.
- Cybercriminals exploit IPs to launch attacks, steal information, or impersonate users.
In other words, your IP address is like your digital footprint, which can easily be used for tracking, profiling, or targeting if not well-protected.
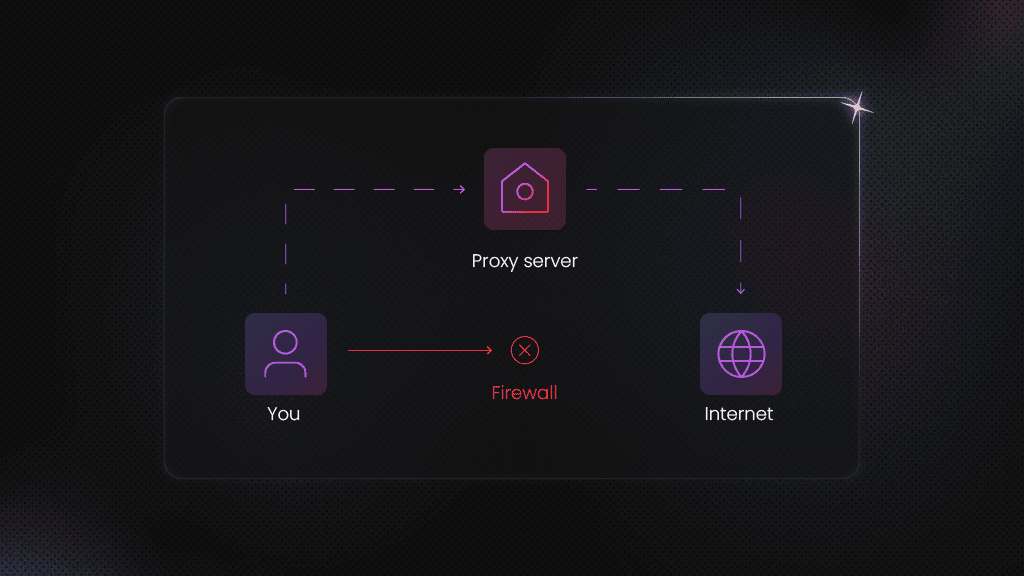
Why you should avoid free proxies and fake IP generators
While saving money is appealing, you shouldn't ignore the serious risks associated with free proxies and fake IP solutions.
Free proxies and VPNs
Free proxies or VPNs may seem convenient, but they often come at the cost of your data and privacy. Many of these services log your activity and sell your data to third parties. Potential threats include:
- Exposed financial details, like credit card or bank login information
- Location data is being tracked and sold.
- Activity logs shared with unknown third parties
- Malware injection through compromised proxy servers
Free services are often built as a honeypot scam to collect users’ personal data, lacking robust security measures, which makes them an even easier target for hackers.
Fake IP generators in 2026: how they work and why they’re misunderstood
Contrary to popular belief, there’s no such thing as a real “fake IP” that can hide your identity online. What most people call “fake IP generators” are actually network simulation tools used by developers, and not privacy solutions.
Here’s how they work:
- Algorithmic simulation. These tools create IPs that mimic valid IPv4 or IPv6 structures for safe testing.
- AI validation. Many tools used in 2026 are integrated with AI to ensure that generated IP addresses avoid conflicts with real network ranges.
- Safe environment testing. Developers use them to simulate traffic, test APIs, or configure networks without making a real internet connection.
Now, let’s take a quick look at the differences:
Type
Description
Purpose
Real network connection
Mock IP
Automatically generated IPs that replicate the structure of real IPs for software testing.
Used for testing applications or security setups.
No
Dummy IP
Non-functional IPs that exist within reserved ranges are used as placeholders.
Safe simulations and internal configurations.
No
Residential IP
Real IPs assigned by ISPs to genuine devices and users.
Secure browsing, web scraping, ad verification, and geo-specific access.
Yes
Bottom line – fake or generated IPs are for developers, not privacy seekers. If your goal is anonymity, residential or rotating proxies are the correct tools.
Which proxy server can change your IP?
Now that we’ve clarified that free proxies and fake IP generators are not the best choices if you value your privacy and want the highest level of anonymity, it’s time to explore the best options for changing your IP address.
Rotating proxies
Rotating proxy networks are the best option when you need a different IP address. A robust rotating residential proxy network is the only IP faker that can work on a massive scale and still successfully hide your IP address while increasing your privacy.
Dedicated proxies
Another reliable option for changing your IP address is a dedicated proxy. A dedicated proxy is an IP address exclusively assigned to a single user, ensuring no other individual shares it. This exclusivity offers increased speed, reliability, and anonymity, making it ideal for activities that require consistent performance, such as managing multiple accounts and accessing geo-restricted content, or for tools like web scraper. Since the IP address is static and solely yours, it reduces the likelihood of being flagged or blocked for suspicious activity.
Residential proxies
Residential proxies use IPs that Internet Service Providers (ISPs) assign to real devices in specific locations. These proxy servers are highly effective for changing your IP address because they mimic legitimate user behavior, making it extremely difficult for websites or services to detect them as proxies. Residential proxies are handy when bypassing geo-restrictions, verifying localized content, or gathering data from websites with advanced anti-bot mechanisms.
Datacenter proxies
Datacenter proxies are another common way to change your IP address. These proxies originate from data centers rather than residential ISPs. While they’re faster and more cost-effective than residential proxies, they’re also easier to detect by sophisticated anti-proxy measures, meaning there’s a higher chance of getting blocked. Datacenter proxies work well for non-sensitive tasks like accessing geo-restricted websites or automating tasks where high anonymity and authenticity aren’t a priority.
Common IP-related risks
Cybercriminals use various techniques to exploit systems and manipulate users. These include IP spoofing, phishing, and IP grabbing, which compromise privacy, disrupt services, and steal sensitive data.
IP spoofing
IP spoofing is a sketchy tactic when cybercriminals disguise their location using someone else’s IP address. This technique is commonly employed in DoS and DDoS attacks:
- DoS (Denial of Service) attacks occur when a server is deliberately flooded with excessive traffic, consuming its resources and bandwidth until it becomes unresponsive or completely unusable. This type of attack is typically carried out by a single source and is designed to disrupt the normal functioning of a website or service.
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks work on the same principle as DoS attacks but are far more powerful and harder to mitigate because they’re launched simultaneously from multiple devices. These devices, often part of a botnet controlled by the attacker, generate overwhelming traffic from numerous locations, making it significantly more difficult to identify and block the malicious traffic without affecting legitimate users.
Phishing
Phishing scams trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details. These scams often involve fake emails or messages designed to mimic trusted sources. Red flags include poor grammar, unfamiliar links, and requests for personal data.
IP grabbing
IP grabbing involves extracting an IP address using third-party tools. While not inherently illegal, it can become malicious if the information is used for extortion or other criminal activities. Ethical uses include:
- Security specialists monitoring for unauthorized access.
- Companies ensuring internal IPs remain secure.
Proxies vs VPNs – which is better?
While both proxies and VPNs offer a higher level of anonymity, their applications are quite different.
Proxies are ideal for businesses and high-volume tasks like web scraping or managing multiple accounts. They provide:
- Unrestricted access to various gated content.
- Enhanced anonymity.
- High scalability for task automation and data collection.
On the other side, we have VPNs. They’re better suited for individual users who want encrypted browsing. However, they lack the scalability and versatility of proxies. Many VPNs also share IPs among multiple users, increasing the risk of detection.
Bottom line
Choosing free or fake IP solutions might save you money upfront, but the risks outweigh the benefits. High-quality proxies from trusted providers offer reliability and security for a long list of online activities.
With Decodo, you gain access to 125M+ proxy IPs from 195+ locations around the globe, and once you’ve got your new IP ready, you can browse the web anonymously, collect data from websites with advanced anti-bot mechanisms, and feel safe and sound.
Try residential proxies for free
Unlock 115M+ IPs from 195+ locations – start 3-day free trial today.
About the author

Benediktas Kazlauskas
Content Team Lead
Benediktas is a content professional with over 8 years of experience in B2C, B2B, and SaaS industries. He has worked with startups, marketing agencies, and fast-growing companies, helping brands turn complex topics into clear, useful content.
Connect with Benediktas via LinkedIn.
All information on Decodo Blog is provided on an as is basis and for informational purposes only. We make no representation and disclaim all liability with respect to your use of any information contained on Decodo Blog or any third-party websites that may belinked therein.