Guide to Web Scraping Airbnb: Methods, Challenges, and Best Practices
Web scraping Airbnb (a global platform for short-term rentals and experiences) involves automatically extracting data from listings to reveal insights unavailable through the platform itself. It's useful for analyzing markets, tracking competitors, or even planning personal trips. Yet, Airbnb's anti-scraping defenses and dynamic design make it a technically demanding task. This guide will teach you how to scrape Airbnb listings successfully using Python.
Dominykas Niaura
Last updated: Nov 17, 2025
10 min read
Why scrape Airbnb data?
Airbnb data helps to understand short-term rental markets, traveler behavior, and property performance across cities. Whether you're an analyst, investor, or developer, scraping Airbnb allows you to collect structured information that isn't directly available through public dashboards or APIs. Here are some of the most common use cases:
- Competitive intelligence. Property owners and rental managers can monitor competitors' listings to analyze amenities, reviews, occupancy rates, and pricing strategies and refine their own offerings.
- Pricing analysis. By tracking nightly rates, seasonal changes, and booking frequency, analysts can determine optimal pricing models for maximizing occupancy and revenue.
- Market trends. Scraped data helps identify emerging destinations, shifts in traveler preferences, and the rise of new property types (such as boutique studios or eco-lodges).
- Sentiment analysis. Reviews and guest feedback reveal what travelers love or dislike about stays in certain regions or property types, which is valuable for both hosts and tourism strategists.
- Personal travel planning. Beyond research, travelers can use scraped Airbnb data to find unique accommodations, filter for hidden gems, or compare pricing trends across multiple destinations.
Challenges of scraping Airbnb
Scraping Airbnb isn't as simple as sending a few HTTP requests. The platform uses a range of technical measures to protect its data and maintain performance for legitimate users:
- Anti-bot and anti-scraping defenses. Airbnb relies on JavaScript-heavy pages, dynamic content loading, and behavior-based detection systems. Without browser rendering, scrapers may fail to load essential elements. In addition, IP blocking and CAPTCHAs are common when traffic appears automated or comes from a single source.
- Changing website structure. Airbnb frequently updates its HTML layout and API endpoints, which can easily break existing scrapers. Maintaining reliable data extraction requires constant monitoring and code adjustments.
- Rate limiting. Even when requests succeed, Airbnb restricts the number of actions or page loads allowed from a single IP or session within a given timeframe. This can lead to incomplete datasets or temporary bans if not managed carefully.
Approaches to Airbnb web scraping
There's no one correct way to collect Airbnb data – your choice depends on technical skill, scale, and how frequently you need updates. In practice, most projects fall into one of two categories: building your own scraper or using a ready-made API service.
DIY custom scraper
If you're comfortable with code, building your own scraper in Python gives you full control over how Airbnb data is collected and processed.
Libraries like Playwright, Selenium, and Beautiful Soup let you load listings, navigate pages, and extract structured details such as titles, prices, locations, and ratings. Playwright and Selenium can both render JavaScript-heavy pages and simulate real user behavior in the browser, while Beautiful Soup parses the resulting HTML for clean, organized data extraction.
A DIY scraper can scale from small research tasks to robust data collection pipelines, as long as you maintain it and adapt to Airbnb's evolving site structure. It demands more hands-on work than using third-party tools, but in return offers flexibility, transparency, and the ability to tailor the scraper to your exact needs.
Using third-party web scraper API services
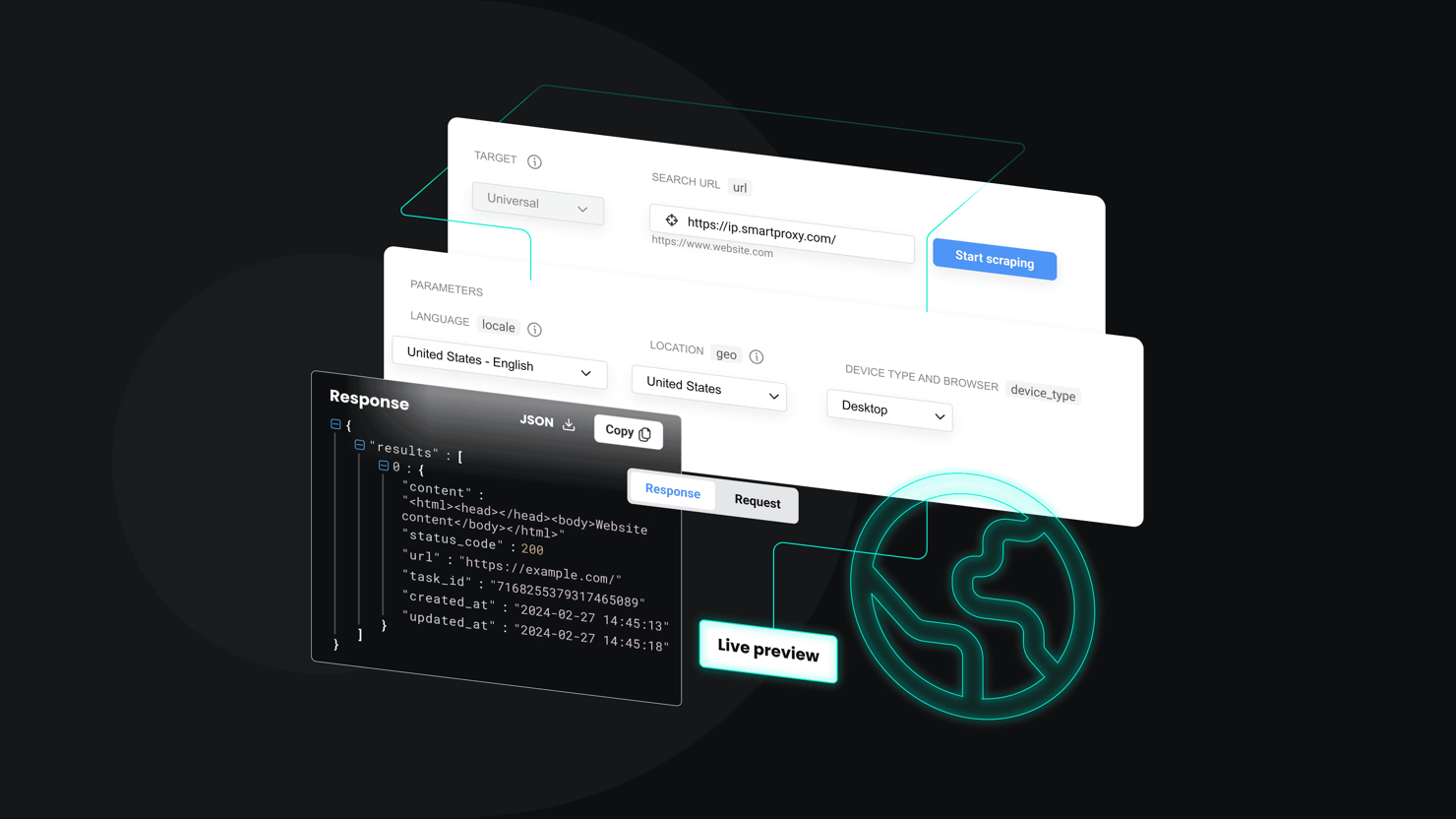
Alternatively, you can rely on scraping APIs that handle the heavy lifting for you – things like proxy rotation, JavaScript rendering, and rate limiting. Services such as Decodo's Web Scraping API let you specify a URL and return data in formats like HTML, JSON, or CSV.
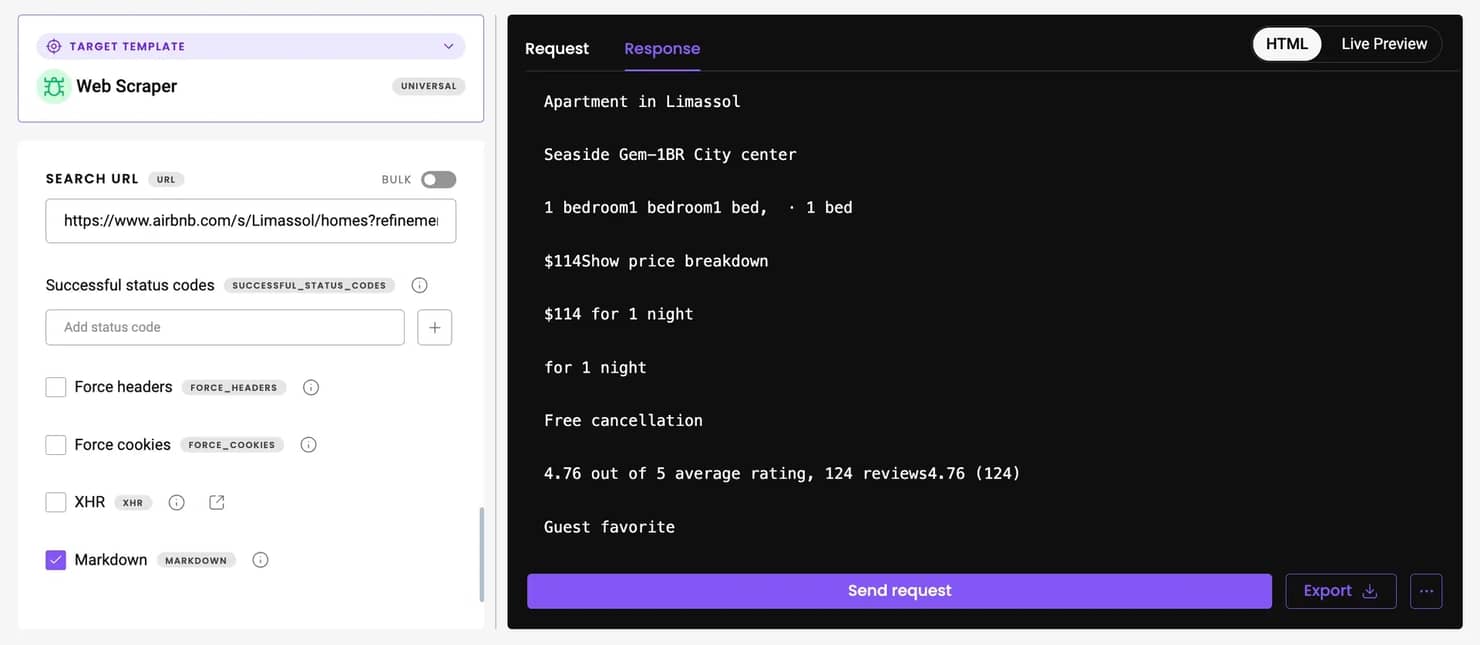
Web Scraping API includes 100+ ready-made templates for popular websites. Since Airbnb isn't one of them yet, you'll need to use the Web (universal) target, which returns the HTML of any page. You can then parse this output using a similar logic as in the Playwright script we'll be building later in this guide.
If you prefer a more readable format right out of the box, enable the Markdown option – Airbnb pages work especially well with it, since they contain little unnecessary markup and present data in a clear, text-oriented structure.
Get Web Scraping API for Airbnb
Claim your 7-day free trial of our scraper API and explore full features with unrestricted access.
Step-by-step guide: scraping Airbnb listings
Let's build a Python scraper that collects Airbnb listing data at scale. This script uses Playwright for browser automation, handles pagination automatically, and includes anti-detection features to keep your scraper running smoothly.
Prerequisites
Before running the scraper, you'll need a few essentials to prepare your environment:
- Install Python. You'll need Python 3.7 or later. Verify your version by running this command in your terminal:
- Install Playwright. The Playwright library powers browser automation. Run the following commands to install it and download browser binaries (Chromium, Firefox, WebKit):
- Other dependencies. The script uses the built-in csv, time, and re modules, so you don't need any additional packages for those.
- Set up residential proxies. Airbnb applies strict rate limiting and anti-bot filters. Using residential proxies helps you stay undetected and prevent IP bans. The sample script below is configured to work with Decodo's residential proxy gateway at "gate.decodo.com:7000," but you can adjust dashboard parameters (such as location, which also determines the currency shown in Airbnb results) to generate a customized proxy string.
Decodo offers residential proxies with a 99.86% success rate, average response times under 0.6 seconds, and a 3-day free trial. Here's how to get started:
- Create an account on the Decodo dashboard.
- On the left panel, select Residential proxies.
- Choose a subscription, Pay As You Go plan, or claim a 3-day free trial.
- In the Proxy setup tab, configure your location and session preferences.
- Copy your proxy credentials for integration into your scraping script.
Get residential proxies for Airbnb
Unlock superior scraping performance with a free 3-day trial of Decodo's residential proxy network.
Finding the data you need
Airbnb loads its content dynamically using JavaScript, so you can't just fetch the page HTML with a simple HTTP request. You'll need to inspect the rendered HTML in a browser.
Open any Airbnb search results page in Chrome or Firefox, right-click anywhere on the page, select Inspect Element, and click on a listing using the selection tool. You'll notice that each property appears inside a <div itemprop="itemListElement"> container. Inside, you'll find data points like titles, prices, ratings, and descriptions spread across multiple elements.
The scraper will target these structures using Playwright's locator system:
- Title and description are extracted from text content within each container.
- Rating and review count are identified with regular expressions matching formats like "4.95 (123)."
- Price data comes from elements with the class umg93v9.
- Listing URLs are taken from anchor tags whose href attributes contain "/rooms/."
To avoid duplicates, the scraper uses each listing's room ID (extracted from its URL) to track which properties have already been collected.
Building the scraper
The scraper is structured around a single class, AirbnbScraper, which keeps logic organized and easy to extend.
- extract_listing_data. This method receives a listing container element and parses its text to extract titles, descriptions, ratings, and prices. Regex is used for numeric fields. If extraction fails, it returns None to maintain data integrity.
- Pagination. The scrape_airbnb method handles navigation between pages. It scrolls to the pagination area, finds the next page link (class c1ackr0h), and loads it automatically. You can adjust the max_pages parameter to control depth.
- Anti-detection measures. To reduce blocking, the scraper launches Chromium in headless mode with stealth arguments, masks the webdriver property via injected JavaScript, sets a random, realistic user-agent string, includes randomized sleep intervals to simulate human browsing, and automatically handles cookie banners.
Saving and using the data
There are many ways to save scraped data, but in this script, the results are stored in a clean CSV file for easy analysis. The save_to_csv() method exports fields like title, description, rating, review count, price, and URL, while excluding internal IDs used only for deduplication. After saving, the main function prints a preview of the first few listings to confirm that the data has been captured correctly.
Once exported, the CSV can be loaded into Pandas for deeper analysis – tracking price trends, rating distributions, or comparing neighborhoods and amenities. This makes it easy to identify top-performing rentals based on ratings and reviews, or to run the scraper regularly and monitor how prices and availability shift over time.
The script is fully customizable: you can change max_pages, update the target URL, or expand the extract_listing_data() method to include additional details like host information or amenities. Its modular structure makes it easy to evolve with your project's goals.
The full Airbnb listings scraper script
You can copy the code below, save it with a .py extension, and run it from your terminal or IDE. After inserting your proxy credentials and the Airbnb search URL you want to scrape, simply launch the script – it will prompt you to enter how many pages to collect. Once the scraping finishes, it will display a small sample of the scraped data in the terminal and automatically save the full dataset to a CSV file for further analysis.
For this example, we’re scraping Airbnb listings for Limassol, Cyprus, during the Christmas holiday period. The scraper collects as many pages as you request and compiles data on titles, prices, ratings, and review counts. By default, the displayed currency depends on your proxy location, but you can override it by appending a parameter like "¤cy=EUR" to your target URL, for example:
Once scraping completes, the output appears as a neatly structured table previewed in the terminal – something like this:
Advanced tips for scaling up
As your Airbnb scraping project grows beyond small experiments, maintaining stability and avoiding detection become key. Large-scale collection requires more than just a simple script – it demands careful attention to proxies, JavaScript rendering, and anti-bot defenses.
Using proxies and rotating IPs
Airbnb actively limits traffic from single IP addresses, so scraping at scale is only sustainable with proxies. Residential ones are the most reliable option, as they make requests appear to come from real users. Rotating IPs periodically (per request or browser session) helps distribute traffic evenly and reduce the risk of rate limiting or bans.
Handling JavaScript-heavy pages
Because Airbnb renders much of its content client side, static HTML requests often return incomplete data. Tools like Playwright or Selenium allow you to fully render pages in a headless browser, ensuring all listings load before extraction. Incorporating smart waiting logic (for example, waiting for certain elements to appear) further improves reliability.
Dealing with CAPTCHAs and blocks
CAPTCHAs are a common roadblock for scrapers that trigger automated traffic detection. Randomized delays, realistic browser fingerprints, and session-based proxy rotation all help minimize the chances of encountering them. If a CAPTCHA does appear, the most practical solution is to pause execution for manual solving or, in more advanced workflows, integrate a CAPTCHA-solving service.
Automating large-scale scraping with APIs
When you're collecting thousands of listings or running daily updates, scaling manually maintained scrapers becomes inefficient. Scraping APIs, such as Decodo's Web Scraping API, automate many heavy-lifting tasks like proxy management, rendering, and retries. While these services come with additional costs and less flexibility, they're ideal for continuous monitoring or large-scale market intelligence projects.
Keeping your scraper up to date
Airbnb frequently updates its website design and underlying code, which means even well-built scrapers can break without warning. Keeping your scraper healthy requires ongoing attention and a proactive approach to maintenance.
Monitoring for website structure changes
Small front-end adjustments (such as renaming classes or changing container hierarchies) can cause your selectors to stop working. To catch these issues early, schedule regular test runs and monitor your logs for failed extractions or missing fields. Setting up lightweight alerts when the scraper returns empty or malformed data can help you detect changes before they disrupt your workflow.
Maintaining and updating your code
Treat your scraper like any other software project. Document how each part works, keep backup copies of your code, and update your selectors or parsing logic whenever Airbnb changes its HTML. It's also wise to refactor periodically: cleaning up deprecated code, improving error handling, and ensuring compatibility with new versions of Playwright or Python. A small investment in upkeep keeps your scraper stable and saves hours of debugging later.
Final thoughts
Following this guide, you've learned how to set up a functional Python scraper using Playwright and residential proxies. Though challenging, scraping Airbnb is well worth the effort for the valuable insights it provides into property trends, pricing strategies, and traveler behavior.
If you prefer simplicity and reliability over customization, our Web Scraping API may be the right choice. It eliminates the need to manage proxies, browsers, and anti-bot handling while still providing full access to Airbnb data in raw HTML or clean Markdown format.
About the author

Dominykas Niaura
Technical Copywriter
Dominykas brings a unique blend of philosophical insight and technical expertise to his writing. Starting his career as a film critic and music industry copywriter, he's now an expert in making complex proxy and web scraping concepts accessible to everyone.
Connect with Dominykas via LinkedIn
All information on Decodo Blog is provided on an as is basis and for informational purposes only. We make no representation and disclaim all liability with respect to your use of any information contained on Decodo Blog or any third-party websites that may belinked therein.