How to Scrape SoundCloud for AI Training: Step-By-Step Tutorial
SoundCloud is a mother lode for AI training data, with millions of audio tracks spanning every genre and style imaginable. In this guide, we’ll show you how to tap into that library using Node.js, with the help of proxies. You’ll get hands-on code examples and learn how to collect audio data for three key AI use cases: music generation, audio enhancement, and voice training.
Dominykas Niaura
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
10 min read
What is SoundCloud?
SoundCloud is a global platform where anyone can upload, share, and stream audio. Since launching in 2007, it’s grown into one of the world’s largest audio communities, hosting over 320 million tracks from artists, podcasters, and creators of all kinds.
What sets SoundCloud apart is its diversity. It’s not just major label music. You’ll find everything from bedroom demos and underground beats to polished albums and niche podcasts. For AI training, that variety is a huge advantage, offering a broad mix of styles, genres, and audio quality to work with.
Why scrape SoundCloud?
SoundCloud offers one of the richest pools of audio data for training machine learning models. Its unique mix of content and metadata makes it especially useful for AI development.
- Diverse audio content. From polished studio tracks to lo-fi bedroom recordings, SoundCloud spans every genre and style. This variety helps train AI models to handle real-world audio.
- Rich metadata. Tracks come with valuable context (play counts, likes, reposts, and user engagement), all of which can add depth to your datasets.
- Community curation. Users create playlists, charts, and collections that naturally organize content by genre, mood, or quality. These curated collections can serve as pre-filtered training datasets.
- Creative Commons tracks. Many uploads use open licenses, making them accessible for research and development.
How to train an AI, ML, or LLM model?
Training an AI model to understand or generate audio isn’t just about feeding it sound. It’s a multi-step process that starts with the right data and ends with careful model tuning. Here’s how it typically works:
- Data collection and preprocessing. First, you gather raw audio files and clean them up. That means converting formats, normalizing volume, trimming silence, and attaching metadata like genre or play counts for added context.
- Feature extraction. Audio has to be turned into something a model can understand. This might mean creating spectrograms, mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCCs), or using raw waveforms, depending on your goal.
- Model architecture selection. The model you choose depends on the task. Music generation often uses transformer-based models (like OpenAI’s Jukebox or Google’s MusicLM), while audio enhancement or classification might rely on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or recurrent neural networks (RNNs).
- Training and validation. You train the model on your dataset through multiple iterations, adjusting weights to improve performance. Validation on a separate test set helps make sure it generalizes well.
Popular platforms for building and training these models include TensorFlow, PyTorch, and JAX. For large-scale jobs, you might also use services like Google Colab, AWS SageMaker, or Paperspace for GPU access.
What you need for scraping SoundCloud
In this tutorial, we'll be scraping SoundCloud artist names, track titles, and download URLs. To do this, we’ll use Node.js scripts powered by Playwright and proxy services to help us navigate SoundCloud’s dynamic, JavaScript-heavy interface.
Here’s what you’ll need to get started:
- Node.js environment. Make sure Node.js version 14 or higher is installed on your machine. (Quick note: JavaScript is the language, while Node.js is the environment that runs it outside your browser.) You’ll also use npm (Node Package Manager), which comes bundled with Node.js, to install required libraries.
- Playwright library. We'll use Playwright to programmatically control a headless browser. It’s perfect for scraping sites like SoundCloud, which rely heavily on JavaScript to load content. Don’t worry – we’ll show you how to install and use it in the examples ahead.
- Basic browser inspection skills. You should know how to open your browser’s developer tools and inspect elements on the page. This helps identify which HTML tags and classes to target in your script.
- Proxies. SoundCloud actively limits automated access. If you're scraping more than just a few pages, a proxy service is crucial. Using residential rotating proxies can help you avoid IP bans and maintain a stable scraping session.
- Storage infrastructure. Audio files can be large, and training datasets often require thousands of tracks. Make sure you have enough local or cloud storage for the number of files you plan to collect.
Why you need proxies for scraping SoundCloud
Proxies are essential for keeping your scraping sessions smooth, anonymous, and uninterrupted. They route your requests through different IP addresses, helping you avoid detection, rate limits, and IP bans from platforms like SoundCloud.
Proxies also let you scale up running multiple sessions at once or accessing geo-restricted content. For this guide, we recommend using residential proxies for the best reliability, but datacenter, mobile, or static (ISP) proxies can also work depending on your goals and budget. Here’s how easy it is to get proxies at Decodo:
- Create a Decodo account on our dashboard.
- Find residential proxies by choosing Residential on the left panel.
- Choose a subscription, Pay As You Go plan, or opt for a 3-day free trial.
- In the Proxy setup tab, configure the location, session type, and protocol according to your needs.
- Copy your proxy address, port, username, and password for later use. Alternatively, you can click the download icon in the lower right corner of the table to download the proxy endpoints (10 by default).
Get residential proxies for SoundCloud
Claim your 3-day free trial of residential proxies and explore full features with unrestricted access.
How to run Node.js scripts
Once Node.js is installed, you'll need a way to write and run your scraping scripts. You can use any text editor with your computer's terminal, or choose an integrated development environment (IDE) like Visual Studio Code, which combines both editing and terminal functionality in one place.
Start by creating a new folder for your project and navigating to it in your terminal. You can do this in any of the following ways:
- Right-clicking the folder and selecting Open in Terminal (Windows/Linux)
- Choosing New Terminal at Folder (macOS)
- Manually running the cd command to switch directories
Next, install the required Playwright library by running this command in your project folder:
Copy one of the script examples from this guide into a .js file (for example, music-gen.js). Don’t forget to replace placeholder proxy credentials (YOUR_PROXY_USERNAME and YOUR_PROXY_PASSWORD) with your actual Decodo proxy details, then update the target URL you want to scrape and any other placeholders such as max tracks, max scroll attempts, or similar limits before running the script.
To run the script, use:
Your terminal or IDE will show live output as the script runs, including results and any errors you might need to troubleshoot.
1. Music generation AI training
Teaching AI to make music is no longer sci-fi. Models can now learn musical patterns, structures, and styles by analyzing existing tracks. This works because music follows both math and culture: it’s structured, yet expressive. That balance makes it ideal for training AI systems to generate coherent, listenable compositions.
Platforms like Suno AI and Udio already let millions create songs from text prompts. Others, like AIVA, Boomy, and Soundful, cater to creators needing royalty-free background music. On the cutting edge, research tools like Stable Audio by Stability AI and OpenAI’s Jukebox show just how deep this field can go.
What to scrape on SoundCloud for music generation training
When targeting SoundCloud for music generation training data, focus on curated collections that represent successful musical patterns within specific genres. Start with official music charts and trending playlists, as these contain tracks that have already proven popular with real audiences.
On the home page of SoundCloud, you’ll find the button Explore trending playlists, which will lead you to the discovery page that showcases playlists of trending, curated, up-and-coming, and other kinds of music. Select the one that matches your direction.
While many chart-topping tracks won't offer direct download options, the metadata and popularity metrics provide valuable insights into what makes music successful. You can often find ways to obtain the actual audio files through legitimate channels outside of SoundCloud once you've identified the most promising tracks.
Scraping SoundCloud playlists
Here's a Node.js script that scrapes metadata from any public SoundCloud playlist:
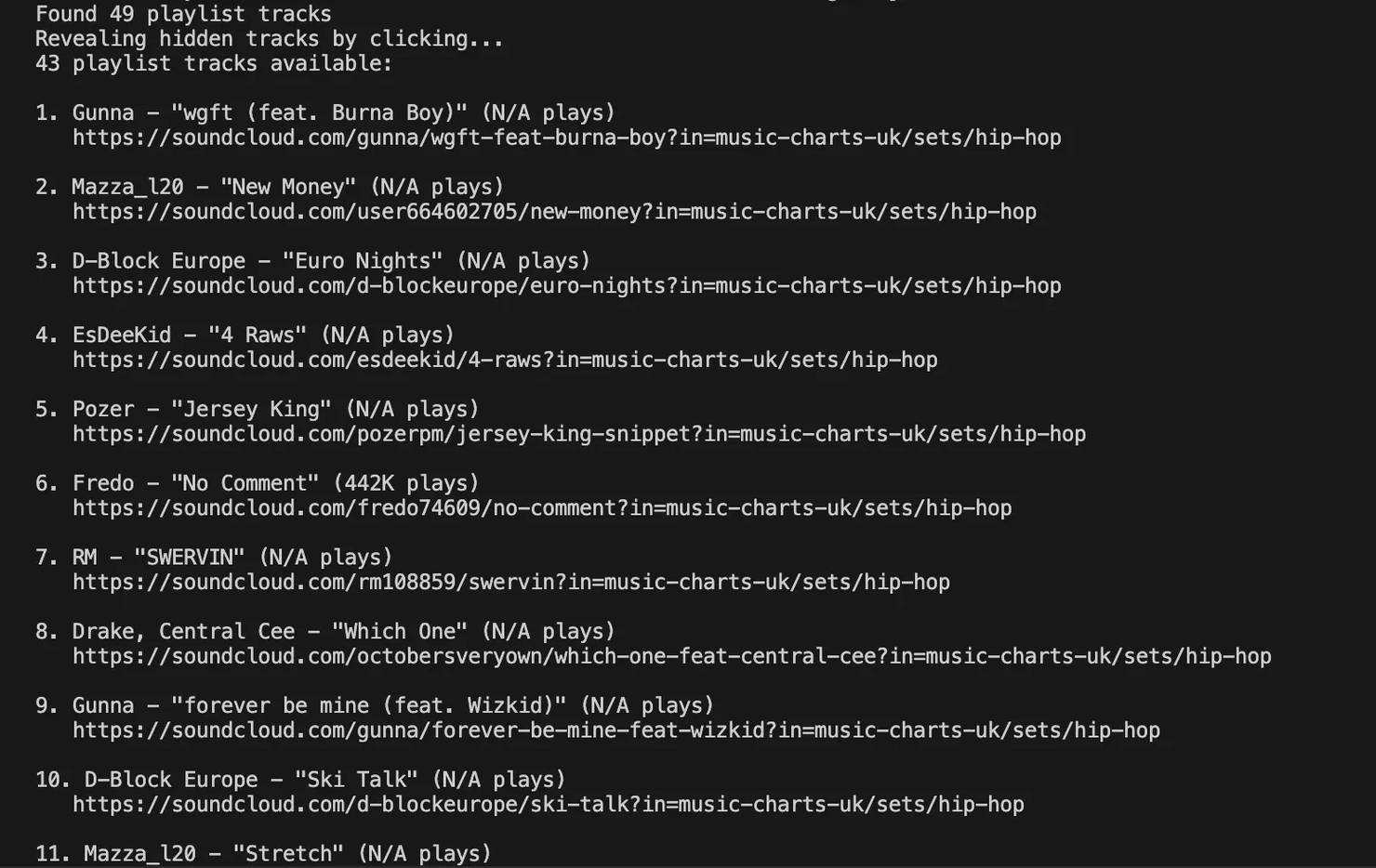
On trending playlists, SoundCloud may hide parts of the tracklist or certain metadata when you’re not logged in. But there’s a workaround: when the script programmatically hovers over each track item, the page reveals track information that isn't visible by default.
When you run the script, it first scrolls through the playlist to ensure all tracks are loaded, then logs how many playlist items were found. Next, it hovers over each track in the list to surface hidden metadata. You can experiment with hover delays, scroll counts, or alternative interaction targets if you want to maximize how much data is exposed.
After that, the script extracts and prints a clean, numbered list containing the artist name, track title, play count (or “N/A” if unavailable), and the full SoundCloud URL. Tracks are sorted by their playlist position to preserve the original order, and all collected data is saved to a CSV file.
SoundCloud also applies geo-based restrictions to some tracks, so results can vary depending on the location of the proxy you're using. This isn't a bug. It can be useful if you want to compare regional availability or differences in popularity across markets.
Next steps toward AI training
With this scraped metadata and URL collection, you can proceed to acquire the actual audio files through legitimate channels, since most trending tracks lack direct download options on SoundCloud. Use the artist and track information to locate purchasable versions on platforms like Beatport, Bandcamp, or streaming services that offer high-quality downloads. Then:
- Convert files to a consistent format
- Extract features like spectrograms, MIDI, or raw waveforms
- Organize your dataset using the scraped metadata
This helps your model learn from high-quality, relevant examples that reflect the musical style you’re aiming to replicate.
2. Audio enhancement AI training
Audio enhancement models are trained to clean up degraded recordings, which involves removing noise, fixing low-quality encoding, and restoring clarity to compressed or damaged files. This use case is especially relevant for content creators, podcasters, and musicians who regularly deal with imperfect audio.
The typical training method is called synthetic degradation: you take clean audio, deliberately degrade it (e.g., by lowering bitrate or adding background noise), then train the model to recover the original. Over time, the model learns what "good" audio sounds like and how to fix the bad.
From podcast noise removal to restoring old recordings, audio enhancement has gone mainstream. Tools like Adobe’s Enhance Speech, Krisp, and Descript offer real-time cleanup for creators, while NVIDIA RTX Voice shows how far the tech can go. Platforms like Auphonic and Cleanvoice even offer fully automated audio cleanup, aimed at non-technical users.
What to scrape on SoundCloud for audio enhancement training
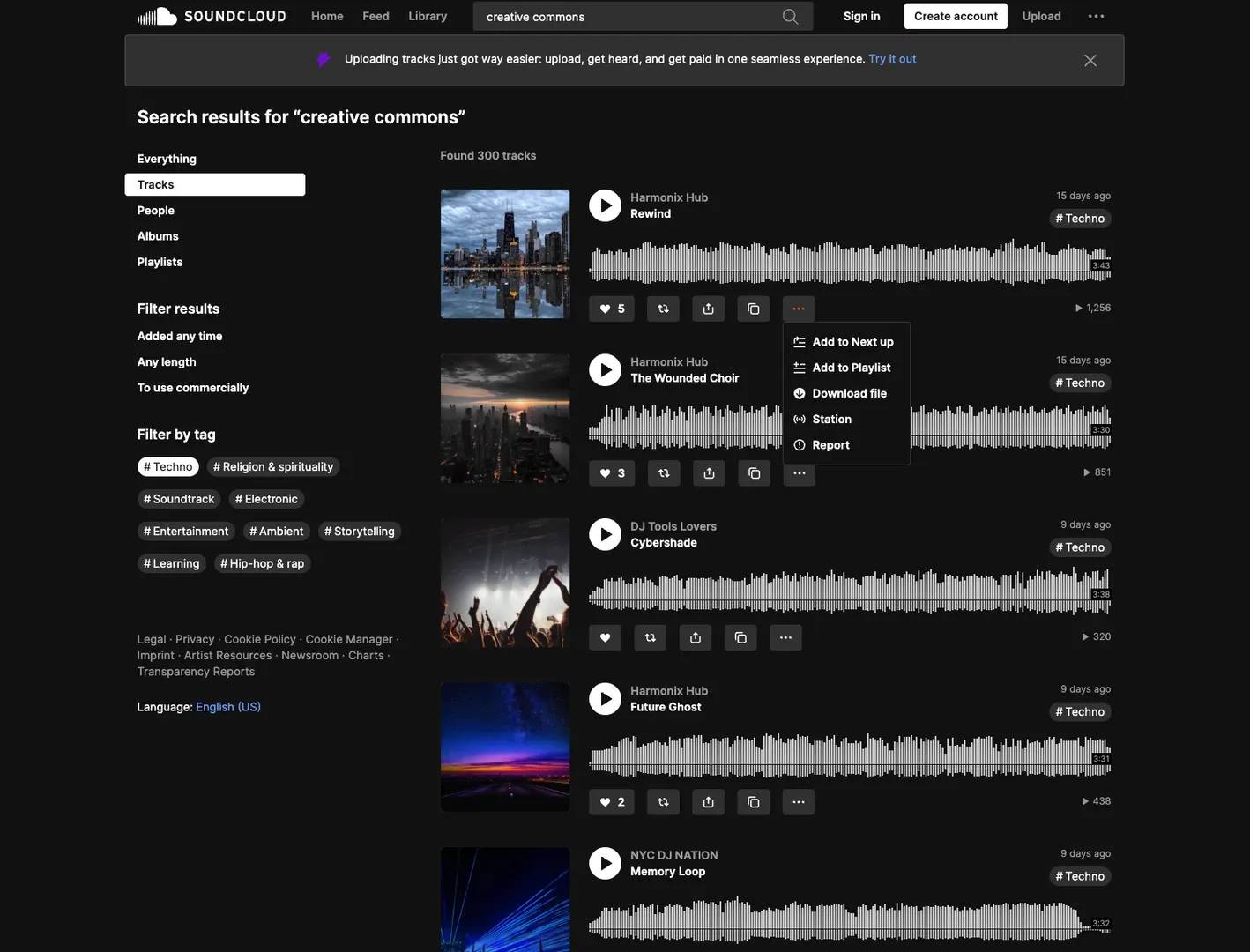
For this use case, you’ll need actual downloadable audio files, not just metadata. Focus on Creative Commons tracks – these are free to use and often include download buttons. In the SoundCloud search bar, try terms like: "creative commons," "CC BY," "free download," or "royalty free".
To refine your results, add time filters to surface recent uploads. Once on a search results page, check a few tracks to make sure the Download file button is available (in the "three dots" dropdown next to the track).
Scraping SoundCloud search results pages
Here’s a Node.js script that scrapes SoundCloud search results and filters for tracks with downloadable audio:
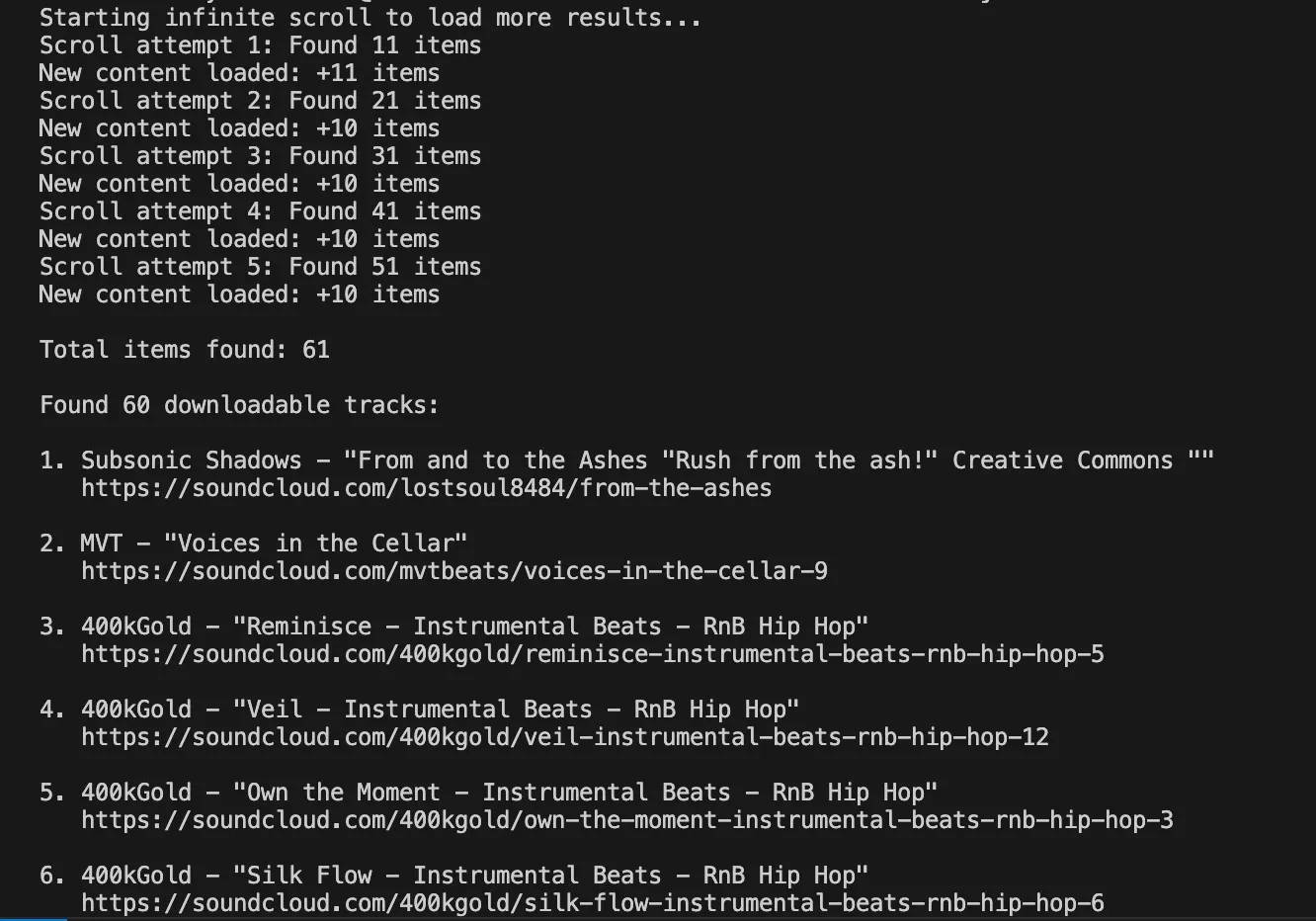
When you run the search results script, it automatically scrolls through the page to load more results. In the terminal, you'll see progress messages like "Scroll attempt 1: Found 11 items" and updates when new content is loaded. This continues until the script reaches the configured scroll limit, hits the target number of results, or detects that no new items are appearing.
Once scrolling is complete, the script goes through each loaded track and checks whether the Download file option is available. This step can take some time, depending on how many items were found and processed.
After the check finishes, the script prints a summary showing the total number of search results and how many tracks have download buttons. The final output is a clean, numbered list with artist names, track titles, and full SoundCloud URLs. All of this data is then saved to a CSV file on your computer.
Creating your training dataset
After scraping, manually download the audio files using SoundCloud's native Download file buttons. These clean tracks will serve as your "ground truth." Next, apply synthetic degradation techniques like:
- Bitrate reduction (e.g., 320kbps → 64kbps)
- Sample rate reduction (e.g., 44.1kHz → 22kHz)
- Noise injection
- Artifact simulation (e.g., compression glitches)
Pair each degraded version with its original, and label them by type and severity. This gives your model a wide range of examples to learn from.
By using a diverse set of Creative Commons tracks, your model will be exposed to different genres, vocal styles, and production levels, helping it generalize better to real-world audio issues.
3. Speech AI training
Speech AI models are built to understand, process, and generate human speech across different accents, languages, styles, and recording conditions. With voice interfaces now everywhere, from smartphones to customer service bots, there's growing demand for models that can handle natural, messy, real-world speech, not just clean, textbook samples.
Tools like Whisper (OpenAI) have set new standards for multilingual speech-to-text, while services like ElevenLabs offer voice cloning used by creators, streamers, and studios alike. Real-time applications such as Otter.ai, Rev, Alexa, and Google Assistant all rely on speech AI trained on diverse, representative voice data. The same goes for language learning apps, accessibility tools, and smart customer support systems.
What to scrape on SoundCloud for speech training
To train effective models, you’ll need high-quality, long-form spoken content featuring real people in real conversations. Some of the best sources on SoundCloud include:
- Podcasts and educational accounts. Think universities, media outlets, think tanks, or institutions uploading lectures, interviews, and panel talks.
- Interview formats. Interviews offer multiple speakers, natural conversation flow, and a range of tones and accents in one recording.
- Language learning channels. These often feature accented English and multilingual content, which is useful for training models on varied speech patterns.
- Audiobook or documentary creators. Their uploads usually provide clean, consistent solo voice recordings, ideal for voice modeling tasks.
- Long-form uploads. Look for hour-long episodes or sessions. These give you natural pauses, rhythm changes, and unscripted speech patterns.
Scraping SoundCloud profile pages
Here’s a Node.js script for scraping tracks from a specific SoundCloud profile, limited to those with enabled downloads:
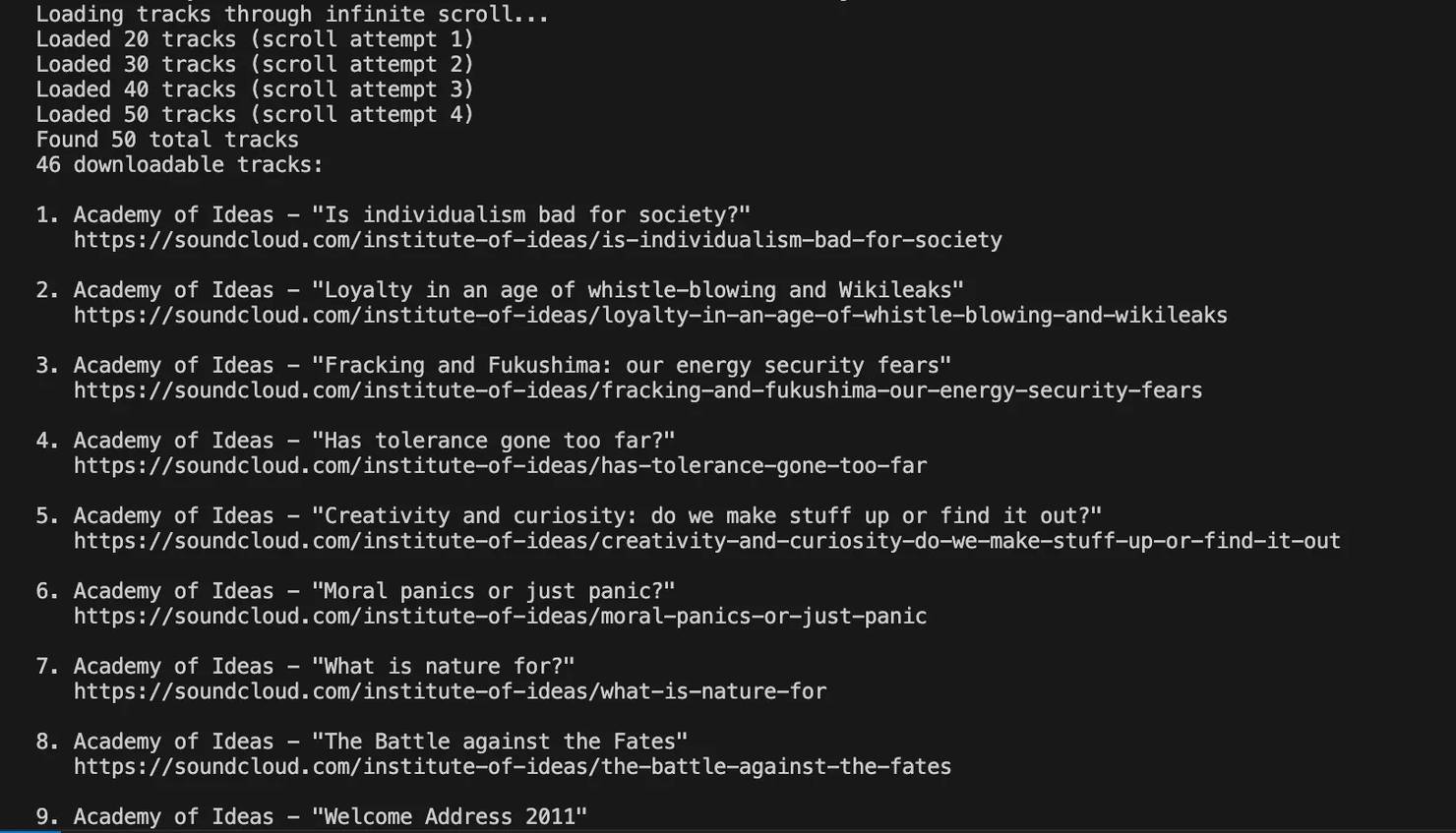
When you run the profile scraping script, the terminal shows the scrolling progress as tracks are loaded from the page. You’ll see updates like "Loaded 20 tracks (scroll attempt 1)" as the script continues until it reaches your configured limit or no new content appears.
Once scrolling is complete, the script reports how many total tracks were found and then checks each one for download availability. After that, it outputs a numbered list containing the creator name, episode or lecture title, and the full SoundCloud URL for each downloadable track. All of this data is also saved to a CSV file.
Preparing the training dataset
After downloading the audio files, you can segment the speech by speaker using speaker diarization tools (or manually, for higher precision). Then:
- Convert to a consistent format and sample rate
- Generate transcripts using Whisper or similar tools
- Tag by accent, gender, speaking style, or context (formal vs. conversational)
Podcasts are especially valuable because they contain natural speech: pauses, overlaps, informal language, and spontaneity. Educational content, on the other hand, provides clear articulation, making it useful for pronunciation learning or voice cloning models.
By combining both types, you’ll get a well-rounded dataset that helps your speech AI handle a wide range of human voices, just like it needs to in the real world.
Best practices for web scraping with Node.js
When scraping SoundCloud data, follow these established best practices to ensure more sustainable data collection:
- Launch reliably. Set realistic HTTP headers, such as User-Agent, Accept-Language, viewport, and generous timeouts. Prefer one browser with multiple pages over many browsers.
- Keep pages light. Intercept requests and abort images, media, fonts, beacons, and manifests to reduce noise and flakiness.
- Navigate with retries. Wrap navigation in a short retry with backoff, wait for result cards instead of fixed delays, then scroll until enough items load.
- Tame popups. If applicable, accept the cookie banner and close the login modal once per context before scraping.
- Use resilient selectors. Combine a few candidate selectors for result cards and avoid brittle single-class matches.
- Pace your actions. Add small random delays, limit concurrent navigations, and slow down when errors spike.
- Recover gracefully. Catch per-item failures, return partial data, and fall back to the track page if the menu path fails.
- Rotate signals when needed. Vary user agents and use quality proxies or sticky sessions if you start seeing many 403 responses.
- Save progress. Append results as you go so restarts resume cleanly, and log only the essentials to guide tuning.
Recent VPN blocks on SoundCloud
In mid-December 2025, SoundCloud confirmed a security incident that exposed private data for roughly a fifth of users, followed by brief denial-of-service disruptions. As part of the response, many VPN and cloud IP ranges began returning 403 errors for a period, which multiple outlets and user reports attributed to tightened filtering during mitigation.
Access largely returned, but similar filters can be reapplied during future incidents. Proxies give finer control over the exit IP and session compared with VPNs. A VPN routes all traffic through one tunnel and one exit IP. A proxy routes only your scraper and lets you choose IPs, rotate or keep them sticky, and target cities or ASNs. Proxies can still be hit by broad filters, but high-quality pools usually give you more ways to adapt. Here's why proxies have the upper hand:
- IP reputation and mix. Residential or ISP proxies typically resemble everyday users more than many VPN exits.
- Rotation control. Rotate or keep sticky sessions per browser context to balance stability and freshness.
- Targeted routing. City or ASN targeting helps sidestep ranges under heavier scrutiny.
Here's how to future-proof your scraping workflows:
- Access check. Request a known public SoundCloud track page (for example, a popular artist’s single) first without a proxy, then with a residential or ISP proxy. For each path send 3-5 GETs, record HTTP status and median TTFB, and pick the path that yields consistent 200s with lower latency and fewer 403s or timeouts.
- Session handling. Use sticky proxy sessions per browser context for multi-step actions like opening the three-dot menu, then rotate to a fresh session between items. Reset a session after N failures or M minutes of use.
- IP rotation. Cycle through diverse residential or ISP subnets. If 403s exceed a small threshold (for example, 3 in the last 20 requests), switch to a different subnet or provider pool automatically.
- Targeting. Prefer consumer ASNs and the cities you actually need. Deprioritize cloud ASNs or subnets that recently produced elevated 403s.
- Pacing. Add exponential backoff with jitter after bursts of 403s or timeouts, and cap concurrent navigations per host.
- Metrics and logs. Record exit IP, ASN, city, status codes, latency, and a simple selector check such as the presence of .moreActions. Use these signals to trigger rotation, session resets, or provider changes.
Final thoughts
SoundCloud offers a huge pool of diverse audio that can power great AI work. With the basics in place you can build datasets for music generation, audio enhancement, and voice or speech training. That is only a starting point, and the same approach can support many other creative ideas.
Results come from the setup you choose and the care you put in. Playwright handles dynamic pages, proxies keep sessions stable at scale, and smart targeting keeps the data relevant. Log your runs, watch for interface changes, and refine as you go. Most of all, remember that data quality often matters more than quantity. A curated dataset of high-quality, relevant audio samples will typically produce better AI model performance than a larger collection of random tracks.
Get high-quality residential IPs
Choose a residential proxy plan from Decodo and enjoy industry-leading performance and reliability.
About the author

Dominykas Niaura
Technical Copywriter
Dominykas brings a unique blend of philosophical insight and technical expertise to his writing. Starting his career as a film critic and music industry copywriter, he's now an expert in making complex proxy and web scraping concepts accessible to everyone.
Connect with Dominykas via LinkedIn
All information on Decodo Blog is provided on an as is basis and for informational purposes only. We make no representation and disclaim all liability with respect to your use of any information contained on Decodo Blog or any third-party websites that may belinked therein.