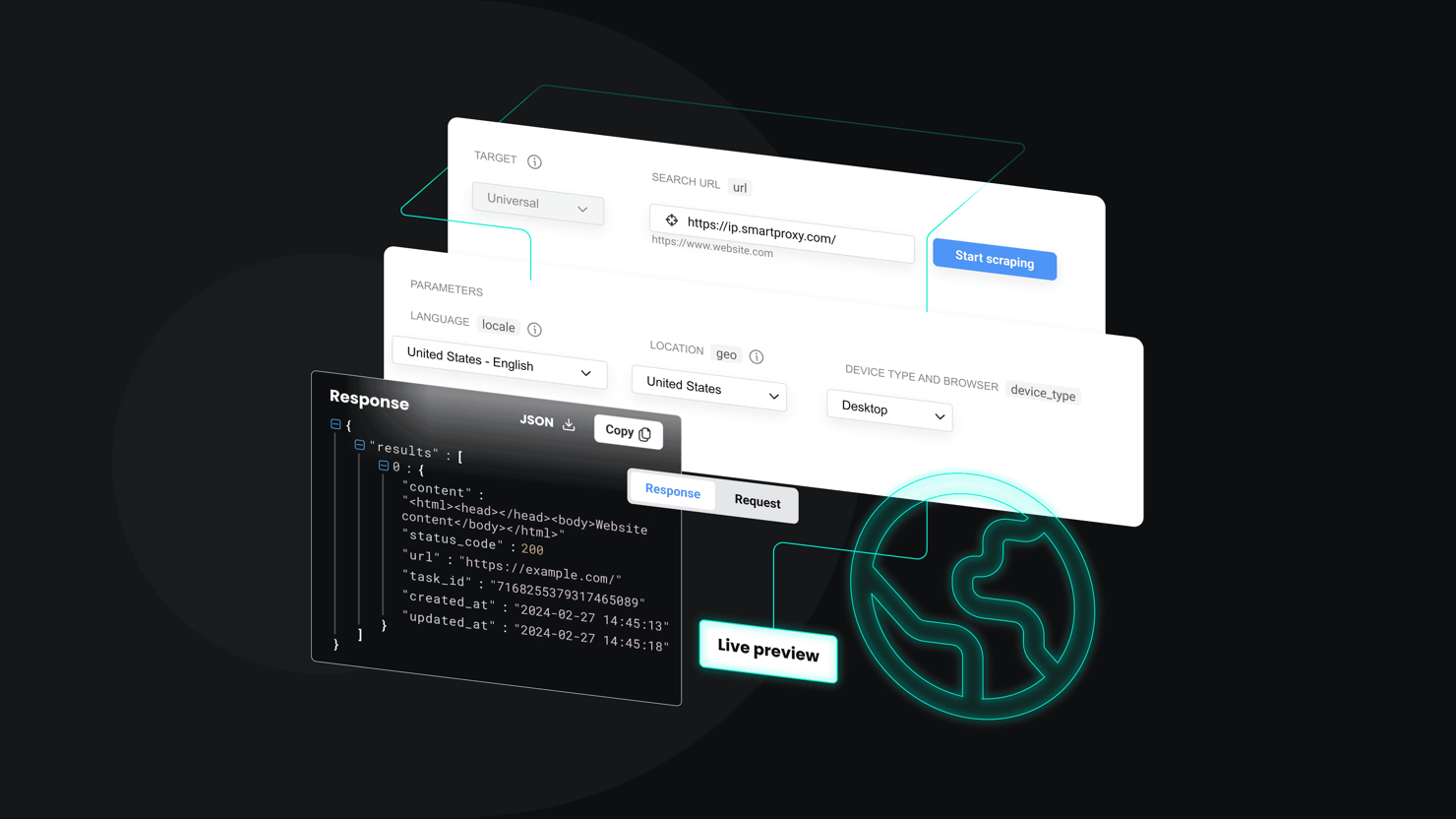
Complete Guide for Building n8n Web Scraping Automations
If you're tired of duct-taping complicated scripts just to grab web data, this n8n web scraping tutorial is for you. You'll see how to use n8n for web scraping, why it beats DIY scrapers, and what you need to get started. Perfect for developers and coding beginners looking to automate data extraction without the headaches.
Zilvinas Tamulis
Last updated: Sep 19, 2025
18 min read
What is n8n?
n8n is an open-source workflow automation platform designed to connect applications, APIs, and databases without requiring excessive custom coding. It provides a visual interface for building workflows, making it easier to design, monitor, and scale automations. With hundreds of built-in integrations, n8n streamlines complex processes, including web scraping, data transformation, and notifications, enabling teams to focus on insights rather than infrastructure.
What is n8n web scraping, and why use it?
n8n web scraping refers to workflows that automate web data extraction from start to finish. Let's dig deeper into how it all fits together.
Understanding n8n features for web scraping
At its core, n8n is built as a complete automation tool. That means it's not just about setting up a workflow to scrape a web page, but also about what to do with the data after it has been retrieved. With n8n web scraping features, you can fetch data, clean it, and instantly send it to a database, spreadsheet, or even a Slack channel.
Compared to traditional scraping scripts, n8n removes the need for error handling, retries, and endless code maintenance. Its visual flow builder makes workflows transparent and easy to adjust, which is a huge benefit for teams that want maintainable automations instead of one-off hacks.
If you're still deciding between n8n and traditional web scraping solutions, consider which one best fits your needs. If you need a quick, lightweight script or very low-level browser automation, consider using tools like Playwright to write your own code. On the other hand, if you're looking for easy scalability, simple integrations, team collaboration, or a less technical and more visual solution, consider web scraping with n8n.
Practical applications of n8n web scraping
Still unsure about using n8n web scraping? Here are a few n8n scraping workflow examples that might inspire you:
- Automated data pipelines. Extract product or market data and push it directly into databases or BI dashboards.
- Content monitoring flows. Track blogs, news sites, or social media platforms and set alerts to trigger when new content matches your criteria.
- Lead generation processes. Scrape business directories or job listings, then enrich and route leads straight into your CRM.
- Price tracking systems. Monitor competitor pricing and set up notifications or auto-updates to your internal tools.
These n8n data extraction methods help teams replace fragile custom scripts with scalable, maintainable automations that keep useful data flowing smoothly into channels that are easy to read and analyze.
Getting started: configuring your n8n scraping environment
Ready to see n8n in action? Whether you're eager to dive right in or just testing the waters, let's walk through how n8n workflows actually work and why they're worth your time.
Installation and initial configuration
Before creating workflows, you'll need to get n8n up and running – either by installing it locally or using the cloud version. Self-hosting provides you with full control over your data, while the cloud option enables you to get started quickly without worrying about server maintenance.
Docker setup
For self-hosted deployments, Docker setup is the recommended approach: it simplifies dependencies and ensures consistency across environments. You'll need to ensure your system meets the basic environment requirements, sufficient RAM, and persistent storage for workflow data. While a Docker setup might sound scary, it's actually quite easy to set up:
- Install Docker Desktop. Download and install the application on your machine.
- Set up Docker. Launch Docker Desktop, log in, and configure your settings. If you're unsure about what to choose, opt for the default settings.
- Run the terminal command. Open your terminal tool and run the following command to install the n8n container. Replace <YOUR_TIMEZONE> with your timezone code.
4. Launch n8n locally. After a brief installation, n8n will be up and running on your machine. If you return to Docker Desktop and then click on Containers, you should see n8n on the list. Click the port number or navigate to http://localhost:5678, and you'll see the n8n dashboard!
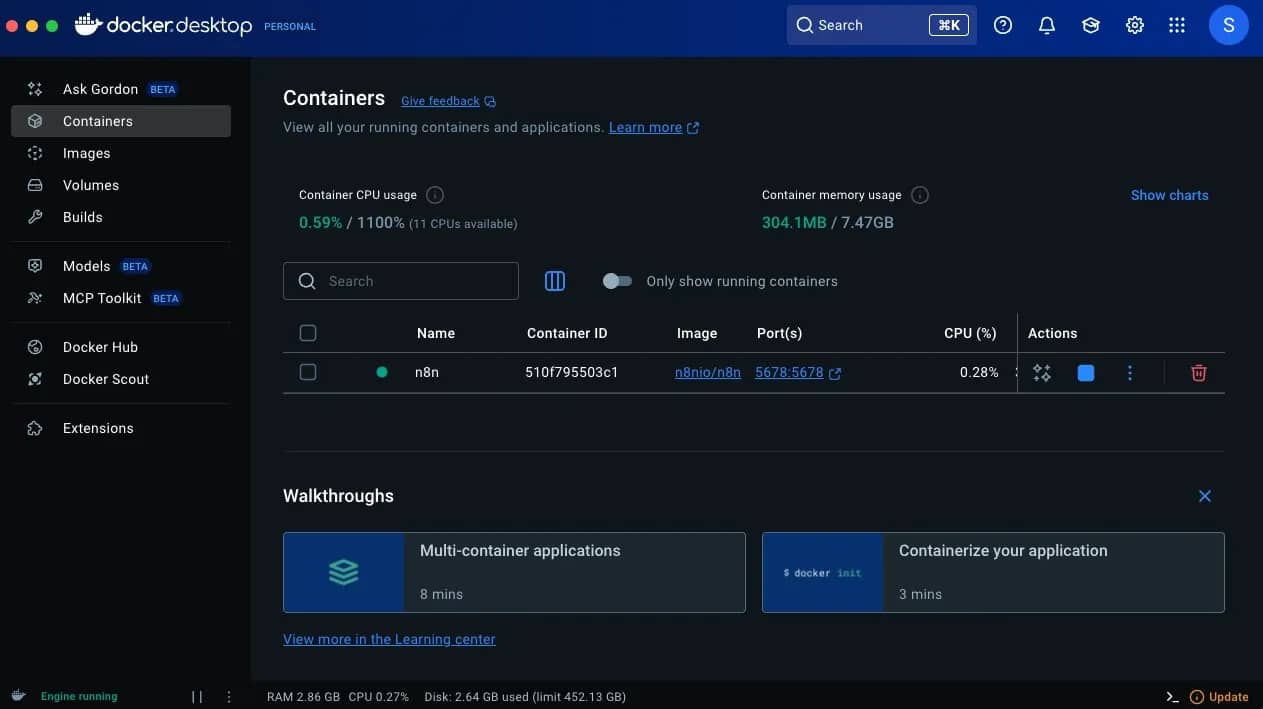
For a more detailed description, refer to the official documentation, which provides advanced setup instructions.
Cloud version
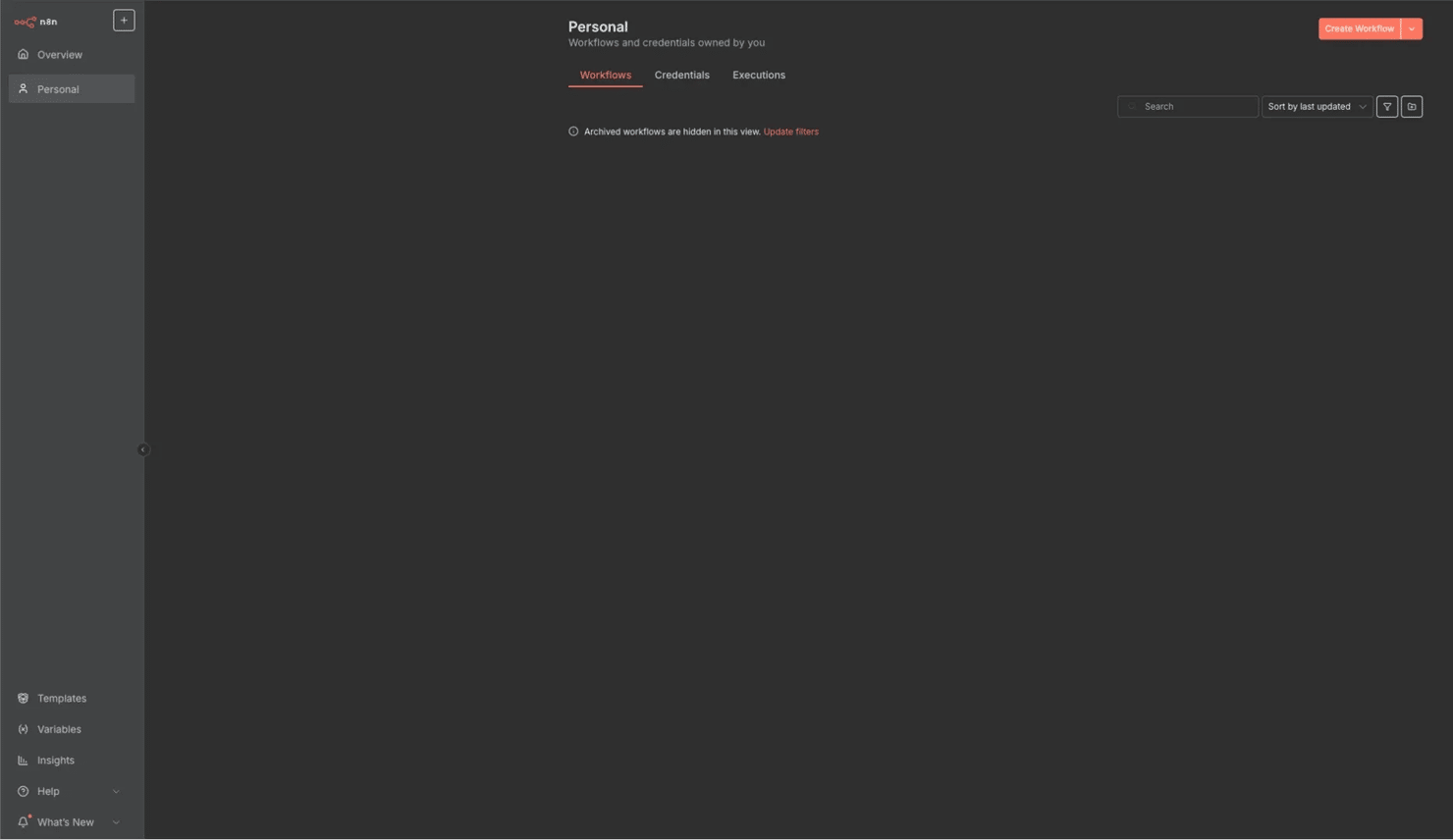
To run the cloud version, simply create an account on the n8n website and start your free 14-day trial (or 1000 executions). After registering, you'll be immediately taken to the dashboard, where you can start creating workflows.
Essential skills before you start
Before diving into n8n web scraping, make sure you're comfortable with a few foundational concepts:
- Understand HTML structure. Knowing how pages are built and understanding elements, classes, IDs, and how to navigate a "div soup" helps you identify the elements you want to scrape.
- CSS selectors and XPath basics. These are your tools for precisely targeting data within the HTML.
- HTTP requests and status codes. Understanding how servers respond will help you debug failed requests and identify errors.
- Rate limiting concepts. Scraping too aggressively can result in your IP being blocked, so understanding throttling and request pacing is essential.
Key n8n components for data extraction
In n8n, a node is a single building block within a workflow that performs a specific action. Each node represents a task, such as fetching data from a website, transforming it, sending an email, or updating a database. Workflows are created by connecting nodes in a logical sequence, so the output of one node can feed into the next.
Here's a brief overview of what kind of nodes exist, what they do, and how they can help in a web scraping workflow:
HTTP Request
The simplest method for an n8n web scraping setup is the HTTP Request node. It lets you fetch data from websites or APIs directly within your workflow. Key features of the n8n HTTP request node for scraping include:
- Method & URL. You can set any HTTP method (e.g., GET, POST, PUT) to make a request to the target URL.
- Headers, cookies, and authentication. Some sites may require these for access; properly configuring them prevents errors and login issues.
- Handling JSON, HTML, and XML responses. n8n can parse various response types, allowing you to extract exactly what you need.
- Retry and error handling. Built-in retry options help ensure that data is retrieved even if there are minor hiccups, while error handling allows you to either stop the workflow or continue along a different path.
- Proxy implementation. You can set a proxy endpoint URL to enter the website through a proxy, ensuring privacy or bypassing geo-restrictions.
Once a request has been sent, the node will return data that can later be passed down to other nodes for data extraction and analysis.
Get the Latest AI News, Features, and Deals First
Get updates that matter – product releases, special offers, great reads, and early access to new features delivered right to your inbox.
HTML
The HTML node's most useful operation for web scraping is Extract HTML Content, which enables parsing of received information. By providing a CSS selector, you can target specific elements and extract data from them. For example, providing a class name will search the HTML document for the first element that matches that class. Other options include:
- Skip certain selectors. If your CSS selector also matches items you don't want to parse, you can provide a list of additional selectors to ignore. For example, if a product has the same class for both the image and title, you can exclude the img tag to only retrieve the product titles.
- Return as an array. To extract all items with the matching selector, you can select Return Array to get the full list of matching elements.
- Multiple field extraction. When extracting more than one value, you can add more values to extract with different CSS selectors.
- Trim values and clean up text. Automatically remove spaces, new lines, whitespaces, and line breaks to tidy up the messy data.
The data is now extracted, cleaned, and ready to use. Together with the HTTP Request node, this covers the most basic approach to scraping and parsing information from a website.
Additional useful building blocks
The beauty of n8n lies in its ability to add useful nodes to an existing workflow, enhancing it further. Here are some of the best nodes for n8n web scraping to help enhance the process:
- Split Out. A list of scraped items is often stored in a single cell, making it difficult to work with. This node can take an array of items and separate them into rows, which simplifies readability, exporting as a file, or to services such as Google Sheets.
- Edit Fields (Set). The node allows you to modify an existing dataset by adding additional rows, columns, and editing fields. Perfect for adding details to a table or manually reviewing data.
- If. To work with conditions, you can use this node to set various logic operators, such as if A is equal to B, if A does not exist, or if A starts with, etc. The A in this case refers to the data received, which is then checked against the logic and branches out to be true or false. You can set further actions for both branches to control how your workflow behaves in specific scenarios.
- Wait. This node is like a traffic light in your workflow, telling the process to stop and wait for a while before continuing. You can set it to wait for a specific time frame, until a certain date and time, or until a specific action is performed. Great for web scraping workflows, as it allows you to add breaks between requests, thereby avoiding server overload and preventing rate limits or IP bans.
- Switch. Very similar to the If node, but allows setting multiple outcome routes instead of just true and false. You can even configure fallback output options when an item doesn't match any conditions, ignore letter cases, and specify how strict the validation should be.
These nodes are essential not only for web scraping with n8n but also for every other type of workflow that requires intelligent routing, conditional logic, and data handling.
Building your first n8n scraping process
Reading about all the cool features means nothing if you don't see them in action yourself. Let's build your very first n8n workflow with this step-by-step guide.
Simple product data pipeline
A simple way to get started with n8n scraping is by building a product data scraper that pulls details from a website about a specific item. It's both a hands-on learning exercise and a solid foundation for more advanced workflows. For this example, we'll use the ScrapeMe test website and get the title and price of the items in the store. Here's how:
- Create a workflow. On the n8n dashboard, click Create Workflow. You'll be taken to the workflow creation interface, where you can start adding and connecting nodes.

2. Add the first step. Click the large + in the middle or the top-right corner to add your first node. Since the workflow needs to know when to start executing actions, this node will tell what triggers the workflow. For now, select Trigger manually so you can launch it with the click of a button.
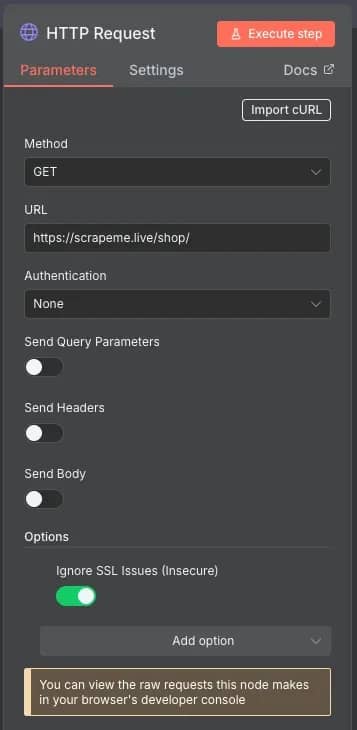
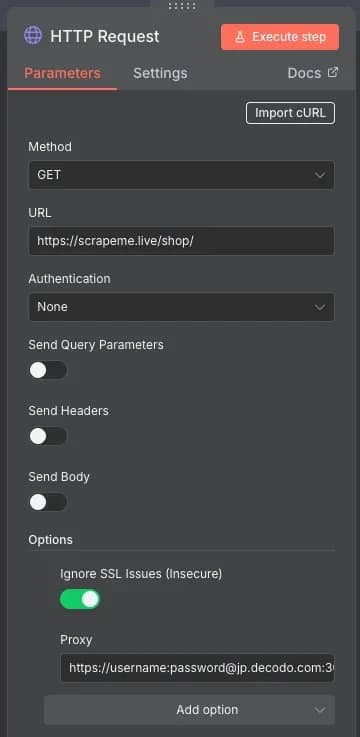
3. Make an HTTP request. To retrieve data from a website, you need to extract its HTML content. You can do this by making a GET request with the HTTP Request node. Click the + on the branch from your first node to add it. You'll see a Parameters window – set the Method to GET, and URL to https://scrapeme.live/shop/. If you encounter an SSL issue, click the Add option button and select Ignore SSL Issues (Insecure).
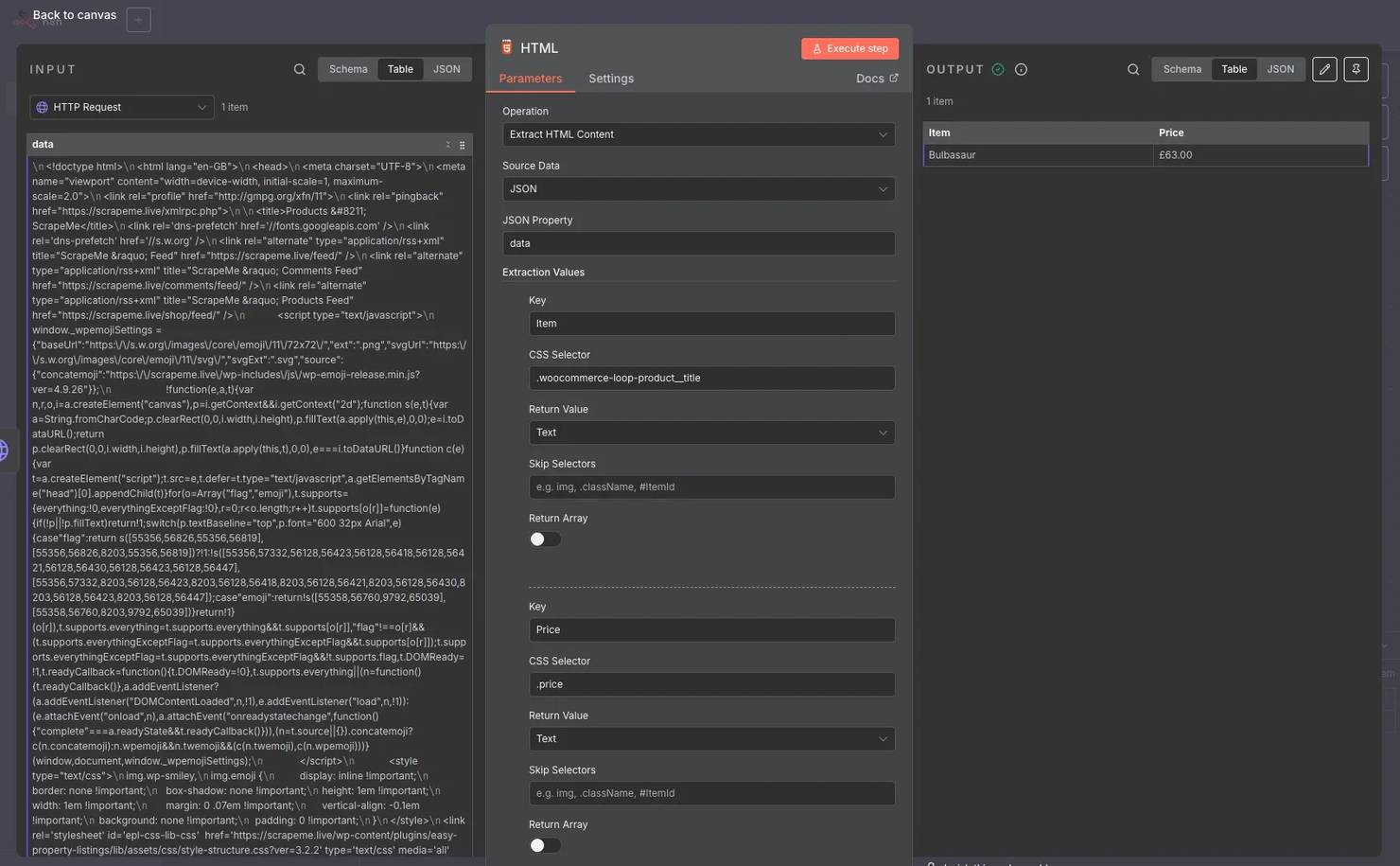
4. Parse the product title. Running the workflow now would just return raw HTML. To extract useful data, add a following HTML node with the Extract HTML Content action. To find the product name, inspect the site – it's inside a ".woocommerce-loop-product__title" class. Set this as the CSS Selector under Extraction Values. Toggle Return Array to get all of the matching values, not just the first one.
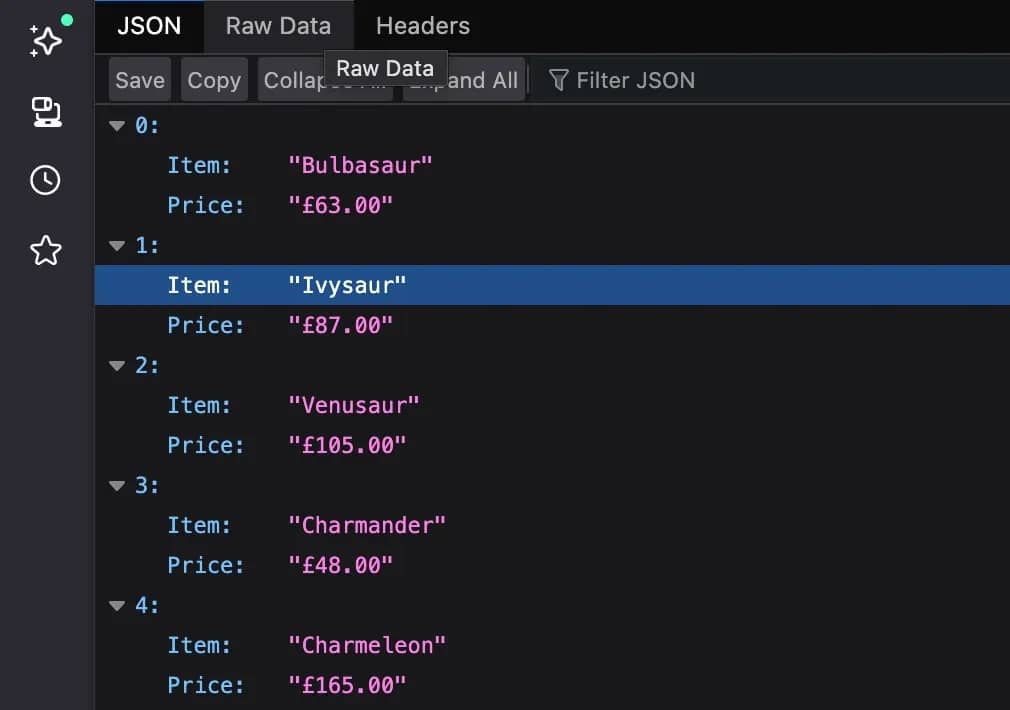
5. Parse the price. In the same window, click Add Value. Repeat the previous step, but this time set the CSS Selector to ".price" to get the price. You can also name the table headers by setting the Key for both columns.
6. Test and debug. Return to the interface and click Execute workflow. You should see the nodes perform actions and light up with a green border if the action was successful. If it's red or returns incorrect data, double-check the input parameters, HTML's structure, or refer to the official documentation for more information.
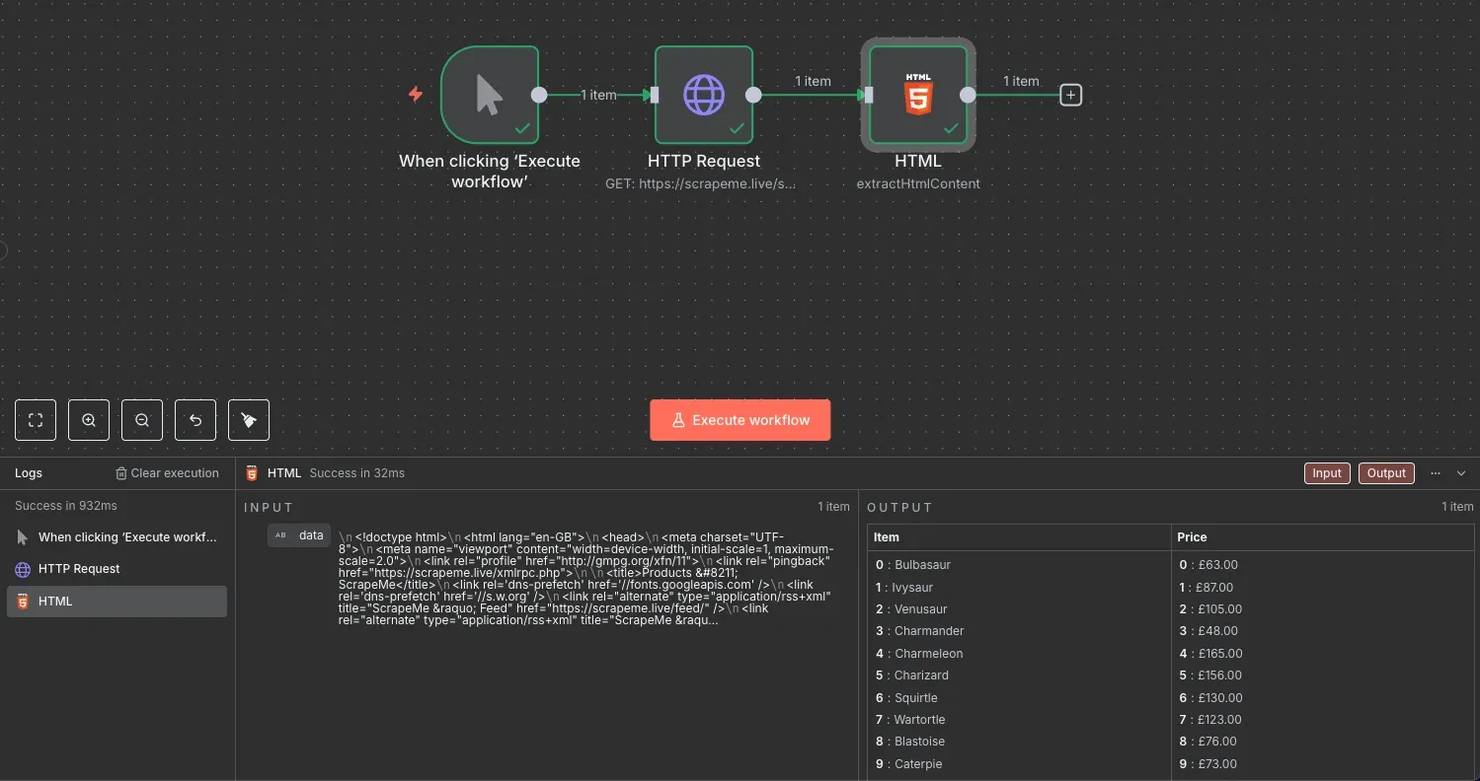
7. Split the data into rows. Since all scraped data currently resides in a single cell, add a Split Out node. In the Fields To Split Out box, enter the column names separated by commas ("Item, Price").
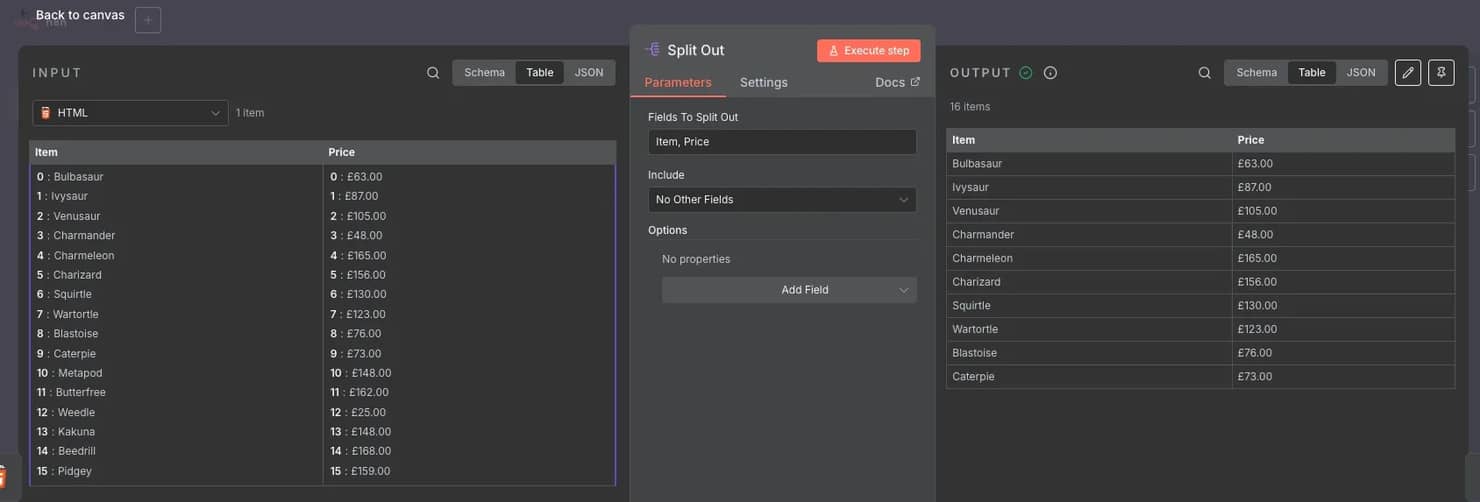
Proxy integration for reliability
While making HTTP requests to test websites is all fun and games, real-world targets don't play around. Making too many automated requests through n8n workflows can trigger limitations, causing your HTTP Request node to fail and return no data.
Fortunately, there's a straightforward way to bypass this – using proxies. When making a request through a proxy, your real IP is hidden, and if it gets blocked, you can simply switch to a new one and try again. Decodo offers numerous options, including trustworthy residential proxies with built-in proxy rotation and location customization.
For n8n proxy integration, you'll need to add an extra option to the HTTP Request node. Click Add option at the bottom and select Proxy. Enter an endpoint URL in a https://username:password@endpoint:port link format. You can easily generate one on the Decodo dashboard that may include location, session type, and rotation frequency parameters.
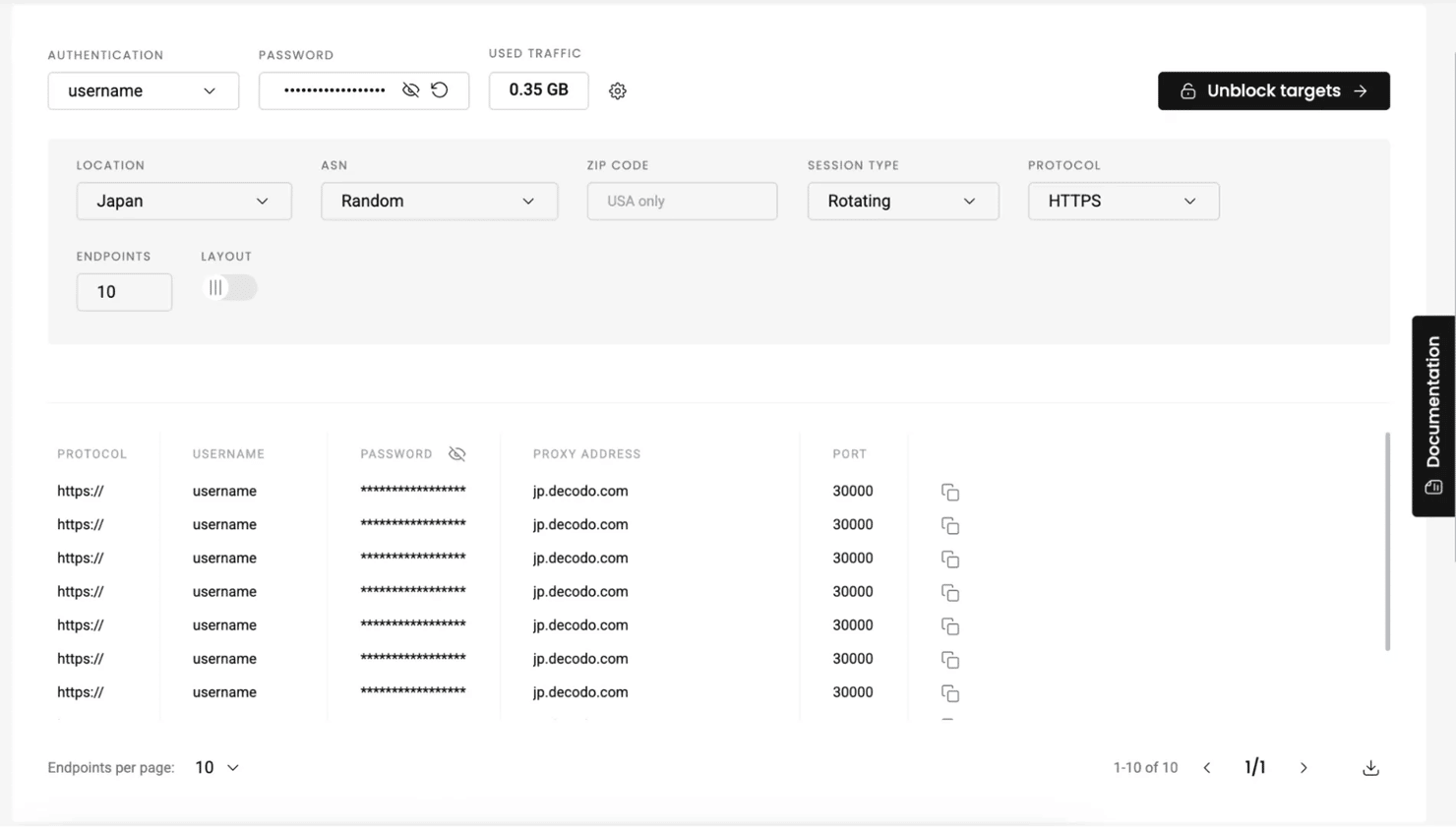
Reliable proxies for your workflows
Get trusted residential proxies to stay undetected and avoid IP bans.
Storing and exporting results
n8n provides several ways to export information through the following methods:
Save to Google Sheets
To export data to a Google Sheets document, follow these steps:
- Add a Google Sheets node. After the Split Out node, add a new one, select Google Sheets, and set the action to Append or Update Row in Sheet.
- Set credentials. You'll need to create OAuth 2.0 credentials and enable the Google Sheets and Google Drive APIs in the Google Cloud Console to allow n8n to access your documents. You can find a full guide on how to do that on the n8n documentation page.
- Create a sheet. Create a new Google Sheets document to store the data and add column headers that match the output column names. These will be used to align the rows correctly.
4. Select and map documents. Return to the n8n Google Sheets node's Parameters page, and select the correct Document and Sheet from the dropdown lists. For Mapping Column Mode, set it to Map Automatically and select the Column to match on to the Item.
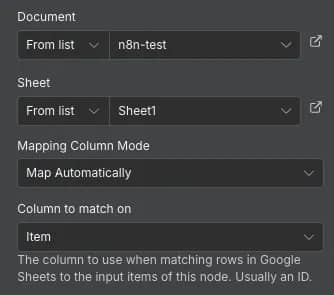
5. Run the workflow. Click Execute step inside the Parameters window or Execute workflow. Check the Google Sheets document to see if all information was exported correctly.
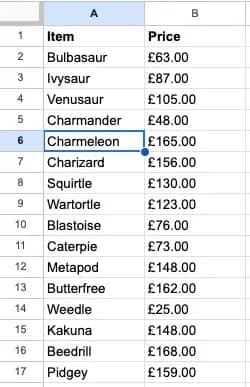
Connect to databases
A database is the most popular method for storing any amount of information. n8n allows you to connect and export data to any databases, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Microsoft SQL. For this example, you'll learn how to do it with MySQL:
- Create a MySQL node. Search for the MySQL node and select the Insert or update rows in a table action.
- Add credentials. Open the node, and set the Credential to connect with. You'll need to provide your database Host, Database name, User, Password, and Port, as well as other optional options like Connection Timeout, SSL, and SSH Tunnel.
- Set parameters. Ensure that the Operation is set to Insert or Update, the correct Table is selected, and the Column to Match On matches the name of the data you're sending.
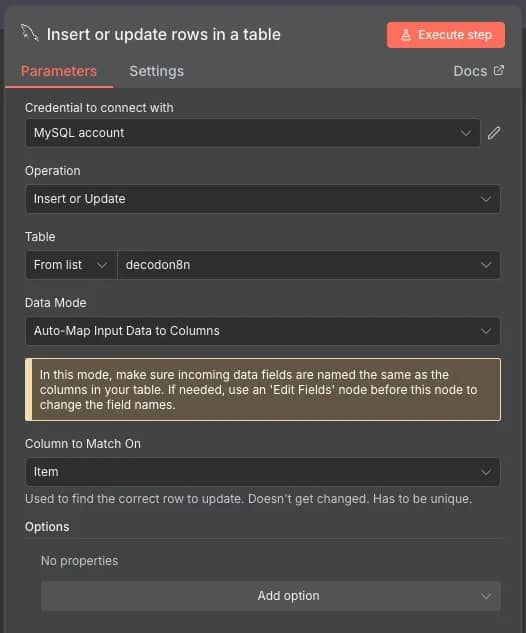
4. Run the workflow. If everything is set correctly, you'll see the new information in your database. Refer to the error log if any issues occur, especially on the database side.
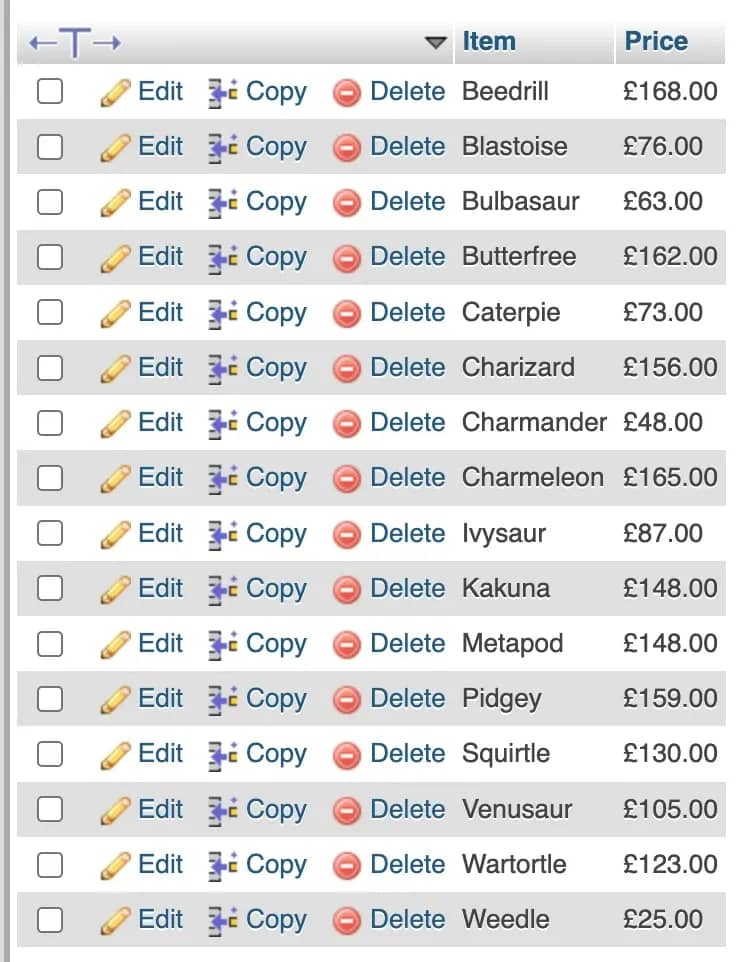
Export CSV/JSON
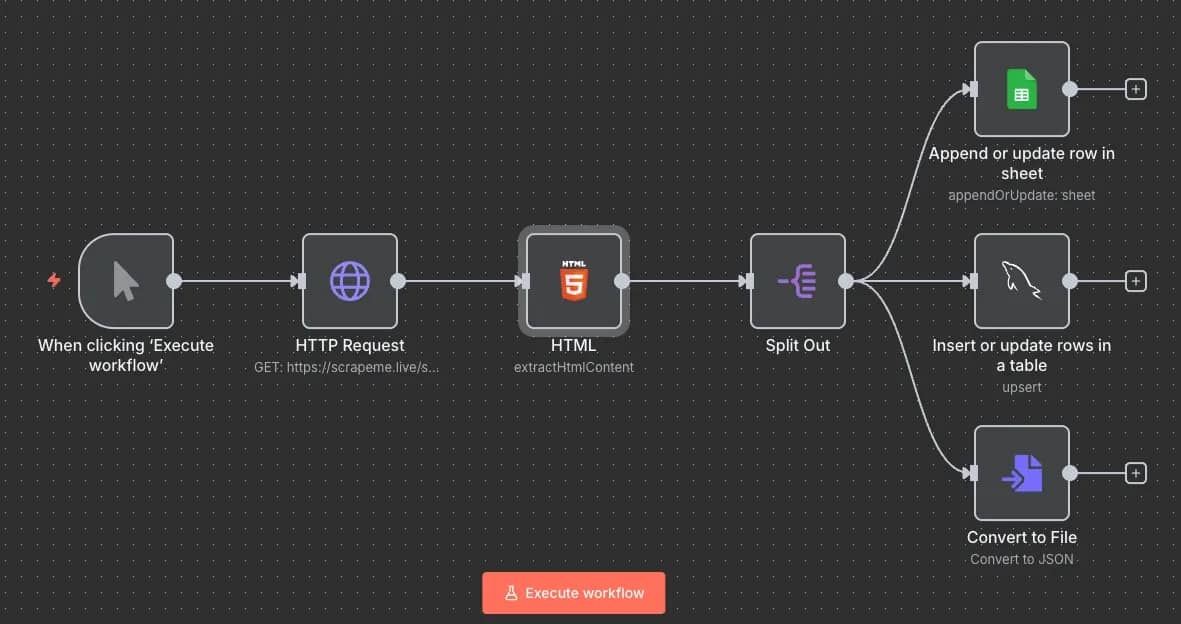
You can export the results in various file formats, including CSV, JSON, HTML, ODS, RTF, and text files. After the Split Out node, simply add a Convert to File node with the Convert to JSON (or a file format of your choice) action. After running the workflow, you can either View or Download the file from the generated output.
Send via APIs
One of the most useful features of n8n is its integrations that allow it to connect to any major service or application to send data. When selecting a node in n8n, check the Action in an app section to see all of the available connections. Most nodes have a Docs link in their Parameters section, so you can read detailed instructions on how to integrate each of them.
You can download the example methods (aside from sending via API) as a JSON file for testing purposes.
Advanced n8n scraping scenarios
Now that you've got the hang of creating workflows and familiarized yourself with nodes, here are a few more advanced workflows that perform specific tasks:
Multi-page extraction with pagination
It's no surprise that many websites, especially eCommerce ones, store their data across multiple pages. Let's have a look at how you can extract information from more than one page with loop nodes and dynamic URL generation.
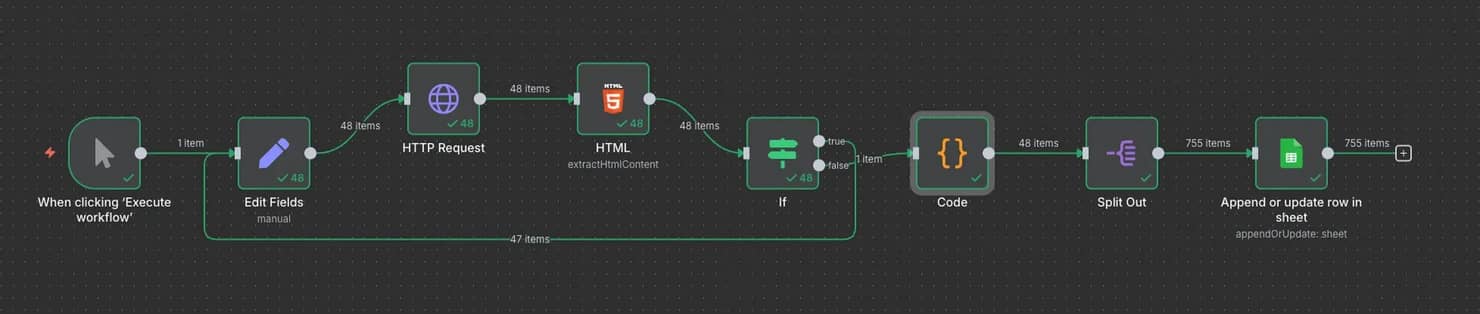
For this example, you'll be scraping the same ScrapeMe website. Create a new workflow, and start adding these nodes in order:
- Trigger manually. As usual, start with the node that allows you to manually execute the workflow with a single button press.
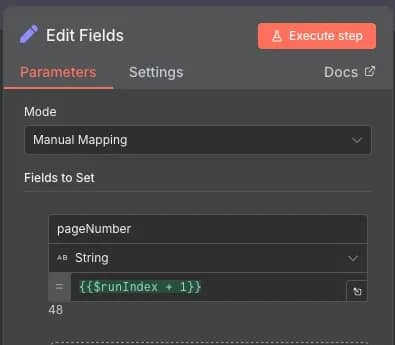
- Edit Fields (Set). You'll need a variable to indicate which page is being scraped. Set the Mode to Manual Mapping and create a pageNumber field with a value of {{$runIndex + 1}}. The $runIndex is a metadata method of n8n that shows how many times the current node has been executed. It's great for incrementation, as it will start at 0 and automatically increase each time it's accessed later through a loop.
3. HTTP Request. Set the Method to GET and URL to https://scrapeme.live/shop/page/{{ $json.pageNumber }}. The curly brackets indicate JavaScript, which accesses the pageNumber variable from the previous node. Don't forget to set a Proxy when scraping more sophisticated websites with anti-bot measures.
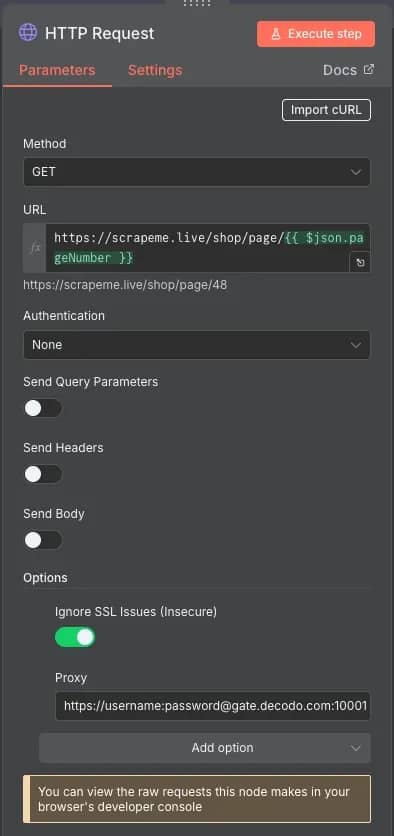
4. HTML. In this node, you'll keep everything the same as the example before. Set the extraction values and CSS selectors for the information you want to parse.
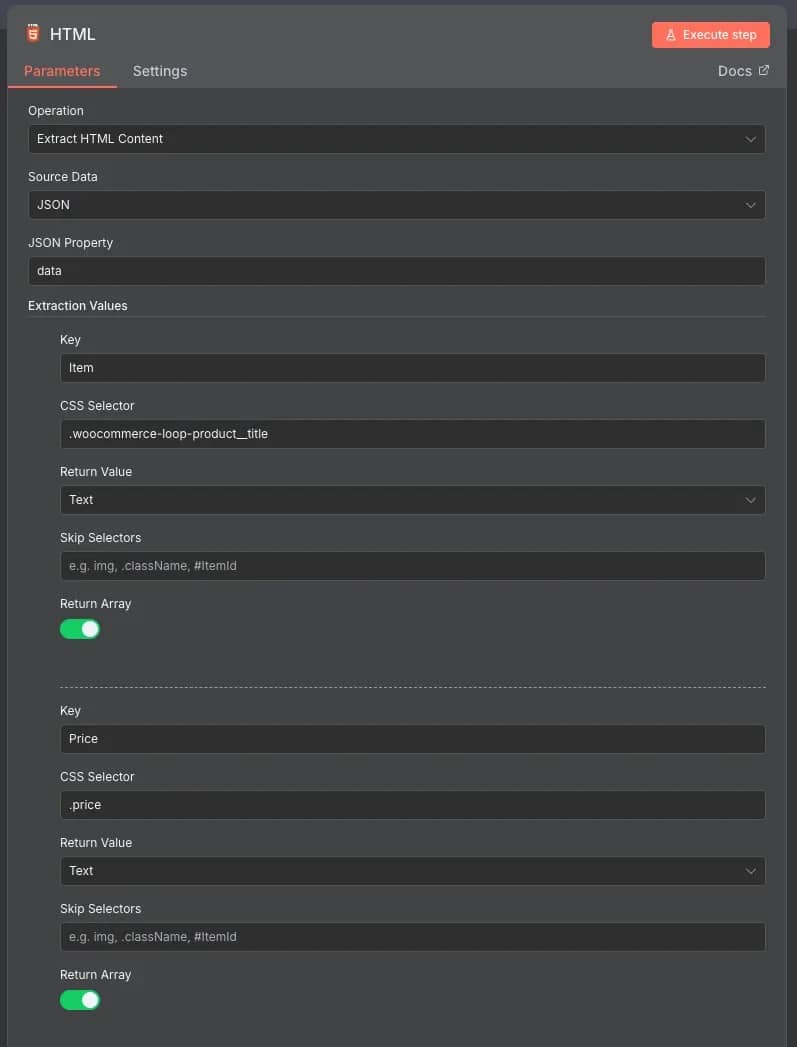
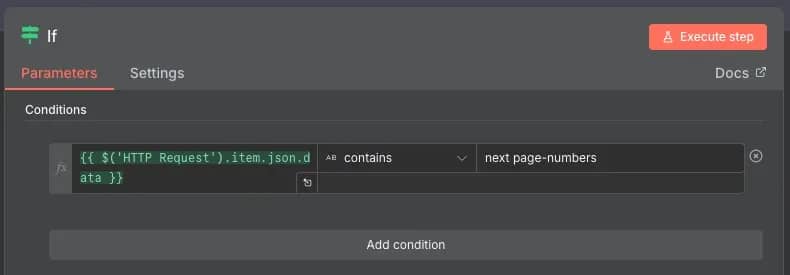
5. If. Checks whether the HTML contains the "next page-numbers" string. It's the two classes of a button that's used to navigate to the next page, and naturally, if it doesn't exist, that means it's the last page. This node will branch into two paths, where True (button exists) will return to the Edit Fields (Set) node and repeat the loop, while False (button not found) will continue after all data has been collected.
6. Code. Once all data is collected, it must be aggregated into a single result. For that, you can use this node to write a simple JS script that will take all of the results each HTML iteration produced and combine them into a single entity.
7. Split Out. The resulting data is still a bit messy, contains index numbers, and places all of the results into a single cell. The node cleans up and separates the data, making it easier to work with.
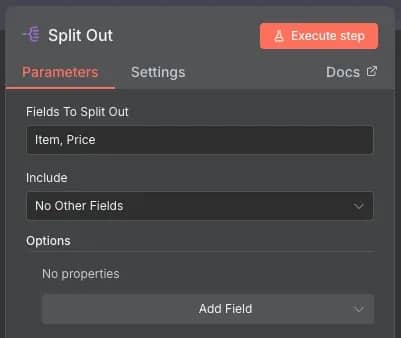
8. Export. You can connect any supported service to send the data or export it in a file format of your choice.
Get started quickly by downloading the full JSON file of this example.
eCommerce price monitoring process
You already know how to scrape an eCommerce site with n8n, but it still lacks a bit of spice. At the end of the day, you won't want to click Execute workflow every time you want to scrape something; you want it to be automated. Here's how to set up a smart eCommerce price monitoring workflow with n8n:
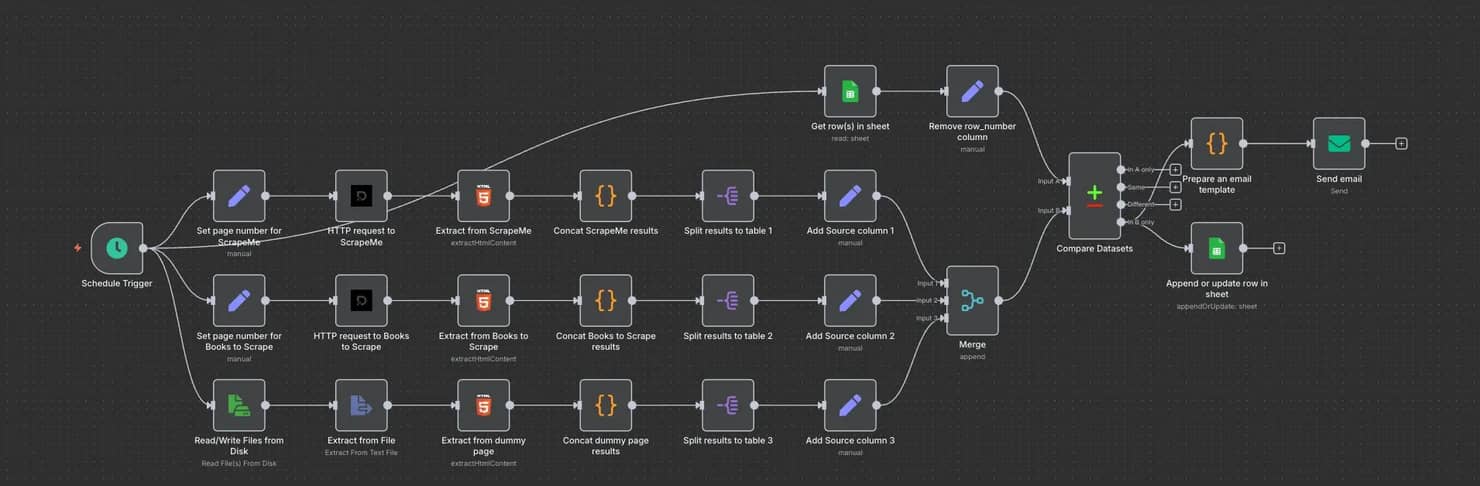
This workflow builds upon the one previously created. Here's a quick breakdown of what it does:
- The workflow begins with a Scheduled Trigger. Instead of running it manually, you can set it to execute automatically at chosen intervals – from seconds to even months.
- When triggered, the workflow splits into three branches, each corresponding to a different source. The first two send HTTP requests through Decodo proxies, while the third reads from a local HTML file. The file is handy for testing changes on an eCommerce site, but it can be swapped out for a live URL.
- Each branch scrapes data, parses it with CSS selectors, and organizes results into tables. All tables are then merged into a single dataset.
- The Schedule Trigger also has an extra branch connected to Google Sheets. It retrieves existing rows, allowing the workflow to compare past data with newly scraped data.
- The Compare Datasets node is the brain of the operation. It checks for differences between the old and new tables. Only new or updated entries (in the In B only branch) trigger further action; if there are no changes, the workflow stops until it's scheduled again.
- A short JavaScript snippet generates an email template listing product updates. The email node then sends alerts about any price changes.
- Finally, the workflow updates the original Google Sheet with the latest data.
As always, you can download the JSON file and test it out yourself. To scrape more than 3 sites, you can create more duplicate branches or create a file that stores all of the URLs and then scrapes them one by one.
Web scraping workflow with AI
The more complex your automation gets, the more your workflows tend to sprawl. Even though n8n is beginner-friendly, a web of hundreds of nodes can quickly turn into a tangled mess.
That’s where the AI Agent node comes in. It’s one of the main reasons behind n8n's popularity. Instead of manually building every branch, you can type a simple chat prompt, and the agent will call an LLM, connect the right tools, and execute the task for you.
Here's an example of how you can use it to scrape the web with Decodo:
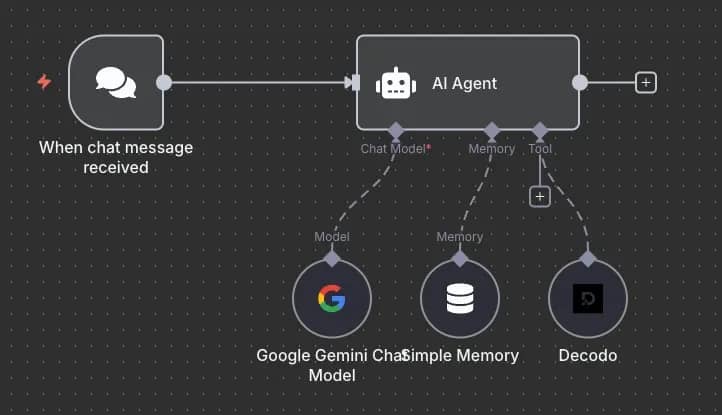
Pretty simple, right? All you need to do is send a message, such as "Scrape me a [website] using Decodo and return the top 3 results", and the AI agent will take care of the rest.
Best practices and performance tuning
Even the best scraping workflows can slow to a crawl if they aren't built with efficiency in mind. To keep things lean, follow these n8n scraping best practices:
Optimizing for efficiency
Build scraping workflows with efficiency in mind by following these n8n scraping best practices:
- Fetch only what you need. Narrow selectors, trim request payloads, and avoid redundant steps.
- Use lightweight nodes. Replace heavy transformations with Function or Set nodes, and batch operations where possible.
- Offload large datasets. Store results in databases, S3, or Google Sheets early to reduce memory usage.
- Parallelize tasks. Run independent steps with Loop Over Items (Split in Batches) or multiple branches to shorten run times.
- Set limits wisely. Define retries and timeouts to manage resources and prevent bottlenecks.
A little n8n optimization upfront saves you from bloated workflows and turns scraping into a manageable task, saving you time and resources.
Overcoming anti-bot roadblocks
Websites don't exactly roll out the red carpet for scrapers. To keep your n8n scraping tools under the radar, you'll need a few tricks:
- User-agent rotation. Configure the HTTP Request node with dynamic headers. Feed it a list of user agents from a previous node (in CSV, JSON, or file format), and rotate them per request to avoid leaving a fingerprint.
- Smart request timing. Add a Wait node to space out requests. Randomizing delays makes your scraper look more like a human user and less like a script.
- CAPTCHA handling basics. There's no guaranteed way to bypass CAPTCHAs. Your best bet is to avoid triggering them altogether by following solid anti-bot practices. In rare cases where you do encounter one, use retries after waiting a short bit of time through a different proxy and user-agent configuration.
- Premium proxy solutions with Decodo integration. Add a Decodo proxy endpoint to your HTTP Request node and you're good to go. Rotation can even be handled at the proxy level by configuring it via the Decodo dashboard, so you don't have to build rotation logic inside n8n. This keeps workflows simpler while still giving you reliable IP diversity.
Try a reliable proxy infrastructure
Leave low-quality proxies behind and switch to enterprise-grade reliability.
Pre-built n8n templates
Ready-to-use workflows
Why start from scratch when you can use n8n workflow automation templates? Pre-built, ready-to-use workflows let you kickstart projects without reinventing the wheel. The template library offers a wide range of common scraping setups, spanning from simple HTTP requests to multi-step data extraction pipelines. Importing them into your instance takes just a few clicks:
- Choose a template. Search for a template that best fits your project. For example, you can search for "scraping" to get workflows for web scraping.
- Examine the workflow. Each template page includes a description and an interactive window that allows you to explore the workflow's structure and ensure it meets your needs.
- Select an export method. Click Use for free and select a method to get the workflow. You can either import it directly into a cloud workspace, a self-hosted instance, or copy it as a JSON file.
- Import to your destination. Once you pick a method, n8n will open your workspace and prompt you to add any required credentials. If you chose the JSON method, just paste the code into a new workflow instance to get started.
- Tweak and modify. The workflow doesn't have to fit your project perfectly. You're free to further customize it or add extra nodes without limitations.
You can get started by exploring workflows that integrate Decodo.
Community resources
The n8n community is an invaluable resource for anyone working with web scraping. n8n Arena showcases contributions from users worldwide, featuring ready-to-use workflows and templates that you can study, adapt, or deploy directly. You can search by keyword and sort by popularity, making it easy to find trusted, widely used workflows.
On GitHub, you’ll find numerous JSON workflow files ready to import, along with community nodes designed for specialized tasks that aren’t available in the standard node library. These resources can save time and help you tackle complex automation scenarios more efficiently.
Finally, the official n8n documentation is comprehensive, well-structured, and includes an AI-powered chatbot for quick answers. The forums are also active and welcoming, with community members and even developers providing guidance, sharing tips, and answering questions. Utilizing these channels can significantly accelerate your learning curve and workflow development.
Conclusion
You've gone from setting up n8n to building your first workflow and even tackling advanced scraping methods. Along the way, we covered roadblocks, debugging hacks, and the best community resources. n8n may have its limits, but it’s a powerful, free playground for automating data extraction and a solid launchpad for building anything you want next.
About the author

Zilvinas Tamulis
Technical Copywriter
A technical writer with over 4 years of experience, Žilvinas blends his studies in Multimedia & Computer Design with practical expertise in creating user manuals, guides, and technical documentation. His work includes developing web projects used by hundreds daily, drawing from hands-on experience with JavaScript, PHP, and Python.
Connect with Žilvinas via LinkedIn
All information on Decodo Blog is provided on an as is basis and for informational purposes only. We make no representation and disclaim all liability with respect to your use of any information contained on Decodo Blog or any third-party websites that may belinked therein.